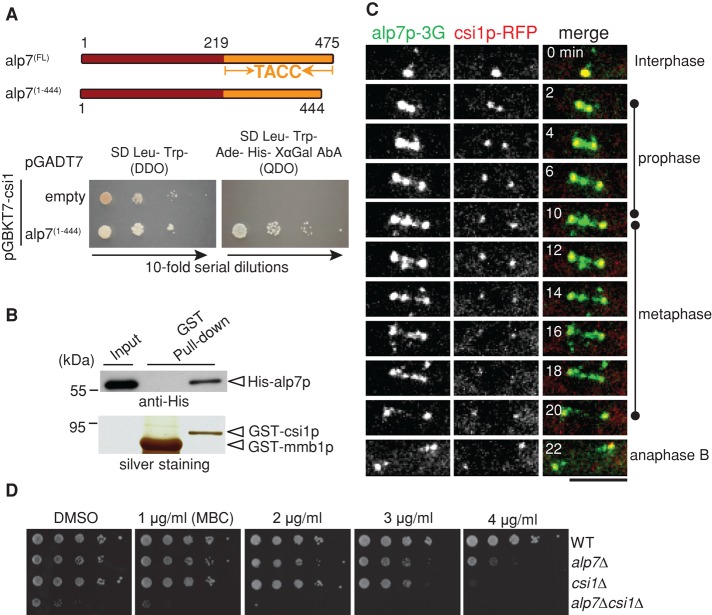
FIGURE 1:
Csi1p interacts with alp7p. (A) Yeast two-hybrid assays testing the interaction between csi1p and alp7p. Y2HGold budding yeasts cotransformed with BD-csi1 and AD-alp7(1-444) or empty AD plasmids were subjected to 10-fold serial dilutions and spotted on SD/–Leu/–Trp (DDO) and SD/–Leu/–Trp/–Ade/–His (QDO) plus X-α-gal and Aureobasidin A (AbA) plates and incubated at 30°C for 4 d. (B) GST pull-down assays. Full-length recombinant proteins GST-csi1p and His-alp7p were produced in E. coli; the precipitation products were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-His antibody. Note that His-alp7p coprecipitated with GST-csi1p, not the control GST-mmb1p. (C) Maximum projection live-cell images of a cell expressing csi1p-TagRFP and alp7p-3GFP from their own promoters. Alp7p colocalized with csi17p at the SPBs throughout mitosis and appeared as distinct dots between the two SPBs during metaphase. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) MBC sensitivity assays. Tenfold serial dilutions of wild-type (WT), alp7∆ (alp7p null), csi1∆ (csi1p null), and alp7∆csi1∆ (alp7p and csi1p null) cells were grown at 30°C for 4 d on YE5S plates containing dimethyl sulfoxide or the indicated concentrations of MBC. Note that cells lacking both alp7+ and csi1+ displayed an additive defect in cell growth.