Table 4.
Interactions between parental history of alcohol problems and former Soviet Union (FSU) immigrant status, and effects on substance use and psychiatric disorders in 1,347 Israeli household adults
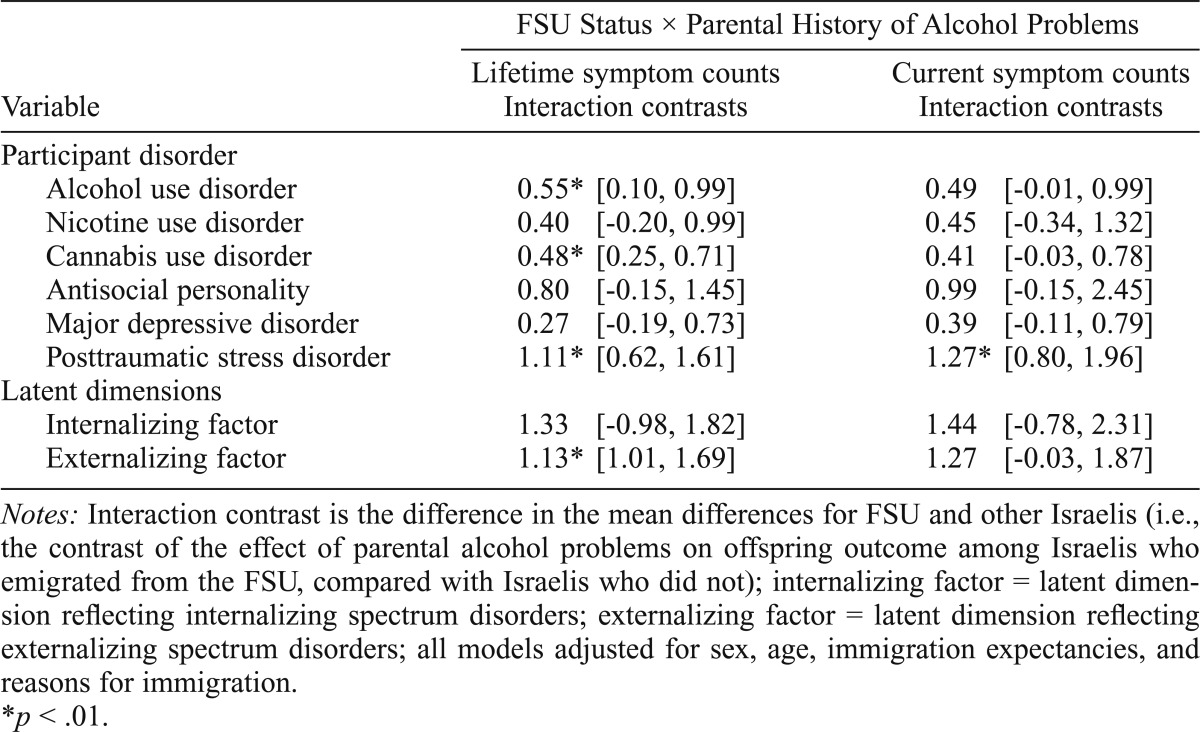
| Variable | FSU Status × Parental History of Alcohol Problems |
|
| Lifetime symptom counts Interaction contrasts | Current symptom counts Interaction contrasts | |
| Participant disorder | ||
| Alcohol use disorder | 0.55* [0.10, 0.99] | 0.49 [-0.01, 0.99] |
| Nicotine use disorder | 0.40 [-0.20, 0.99] | 0.45 [-0.34, 1.32] |
| Cannabis use disorder | 0.48* [0.25, 0.71] | 0.41 [-0.03, 0.78] |
| Antisocial personality | 0.80 [-0.15, 1.45] | 0.99 [-0.15, 2.45] |
| Major depressive disorder | 0.27 [-0.19, 0.73] | 0.39 [-0.11, 0.79] |
| Posttraumatic stress disorder | 1.11* [0.62, 1.61] | 1.27* [0.80, 1.96] |
| Latent dimensions | ||
| Internalizing factor | 1.33 [-0.98, 1.82] | 1.44 [-0.78, 2.31] |
| Externalizing factor | 1.13* [1.01, 1.69] | 1.27 [-0.03, 1.87] |
Notes: Interaction contrast is the difference in the mean differences for FSU and other Israelis (i.e., the contrast of the effect of parental alcohol problems on offspring outcome among Israelis who emigrated from the FSU, compared with Israelis who did not); internalizing factor = latent dimension reflecting internalizing spectrum disorders; externalizing factor = latent dimension reflecting externalizing spectrum disorders; all models adjusted for sex, age, immigration expectancies, and reasons for immigration.
p < .01.
