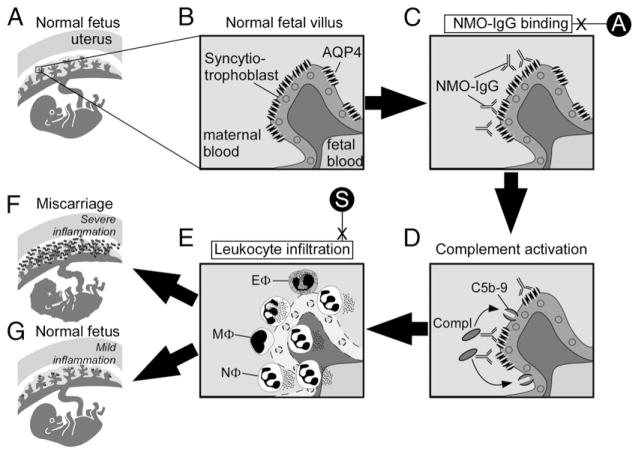
FIGURE 5.
Proposed mechanism of NMO-IgG–induced placental inflammation. (A) Normal fetus in uterus with a (B) magnified view of a normal fetal villus showing AQP4 within the syncytiotrophoblast plasma cell membrane. (C) NMO-IgG binds extracellular epitopes on AQP4 and (D) activates complement causing the deposition of membrane attack complexes (C5b-9) in the syncytiotrophoblast plasma membrane. (E) Leukocytes infiltrate the placenta, primarily neutrophils (NΦ) with some eosinophils (EΦ) and macrophages (MΦ). (F) Severe placental inflammation causes fetal death, but (G) mild placental inflammation allows normal fetal growth. Aquaporumab (A) inhibits NMO-IgG binding, and sivelestat (S) inhibits neutrophil-mediated damage.