Figure 4.
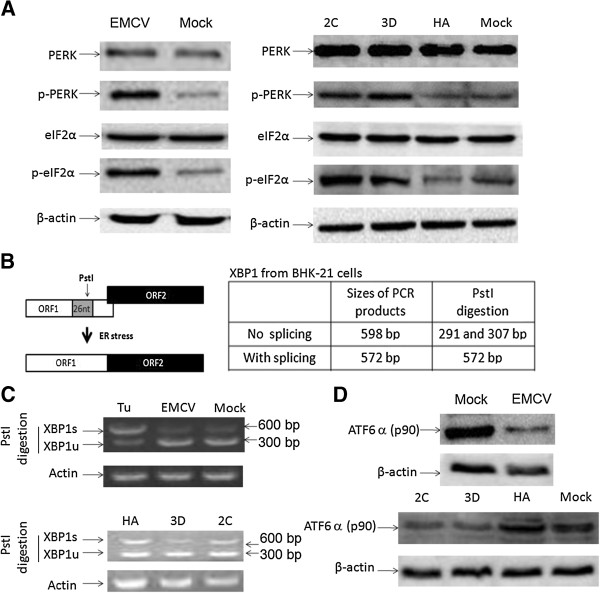
The regulation of the UPR pathway in the EMCV-infected or with expressed EMCV 2C or 3D BHK 21 cells. (A) BHK-21 cells were harvested after infecting with EMCV (MOI = 0.005) for 12 h or transfecting with pCMV-HA-2C, pCMV-HA-3D or pCMV-HA (as a control) for 48 h, and subjected to Western blotting analysis for PERK, p-PERK, eIF2α, p-eIF2α and β-actin with the indicated antibodies. (B) The analysis scheme for XBP1 mRNA splicing. The relative locations of the 26-nt intron and the PstI restriction site are shown. The sizes of PCR-amplified fragments from spliced XBP1 (XBP1s) and unspliced XBP1 (XBP1u) with or without PstI cleavage are also listed. (C) RT-PCR analysis. The BHK-21 cells were treated with Tu (1 μg/ml) for 12 h, infected with EMCV (MOI = 0.005) for 12 h or transfected with the pCMV-HA-2C, pCMV-HA-3D or pCMV-HA (as a control) for 48 h. Total cellular RNAs were prepared, and RT-PCR was performed by using specific primers to determine the XBP1 splicing (XBP1s) level. To detect XBP1 splicing (XBP1s), the PCR products were digested with PstI and electrophoresed. The XBP1u (291/307 bp) and XBP1s (572 bp) bands are indicated. (D) A Western blotting analysis of ATF6α and β-actin in the cell extracts of BHK-21 cells that were infected with EMCV (MOI = 0.005) for 12 h or transfected with 2C- or 3D-expressing plasmid for 48 h.
