Figure 3.
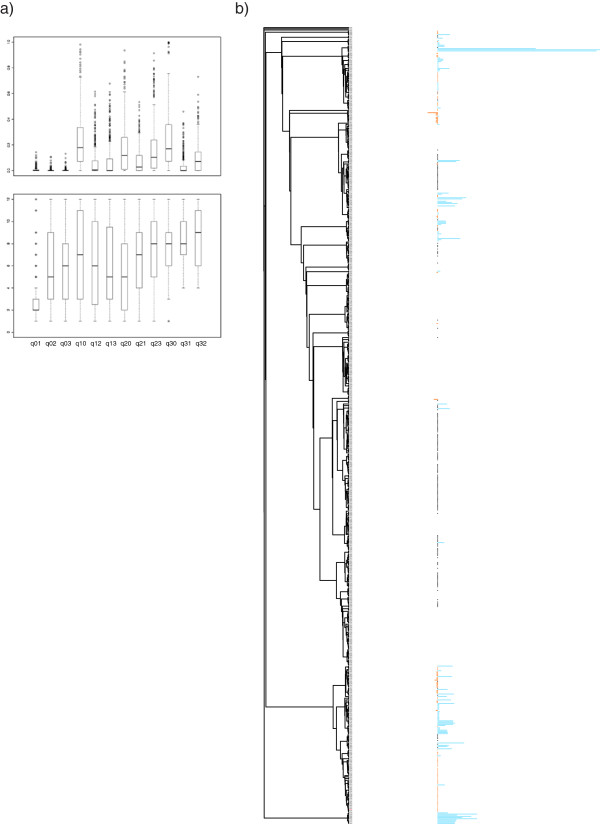
Characteristics of overlapping genes evolution. a) Representation of the transition rate obtained through the BayesTrait analysis of the orthologues of genes overlapping in E. coli. Top - Box plot representation of the normalized values extracted for each gene pairs. Because BayesTrait leads to the generation of transition rates with no upper limits, the normalization allow the comparison of transition rates for the different gene pairs. Bottom - Box plot representation of the order of the different rates (in ascending order) obtained from BayesTrait for each gene pair included in the analysis. b) Example of the observed configuration for one gene pair overlapping in E. coli. The results are presented on the phylogenetic tree build from the 23S rRNA sequences extracted from the different species of interest. The information related to the distance separating orthologues are coded as follow: The segment of DNA forming the overlap for overlapping orthologues is represente in orange, the portion of DNA separating adjacent orthologues is in blue, the orthologues pairs none adjacent are represented by a black dot, and if one or both of the orthologues is missing no mark in made. The length of the segments is proportional to the distance between the two genes of interest.
