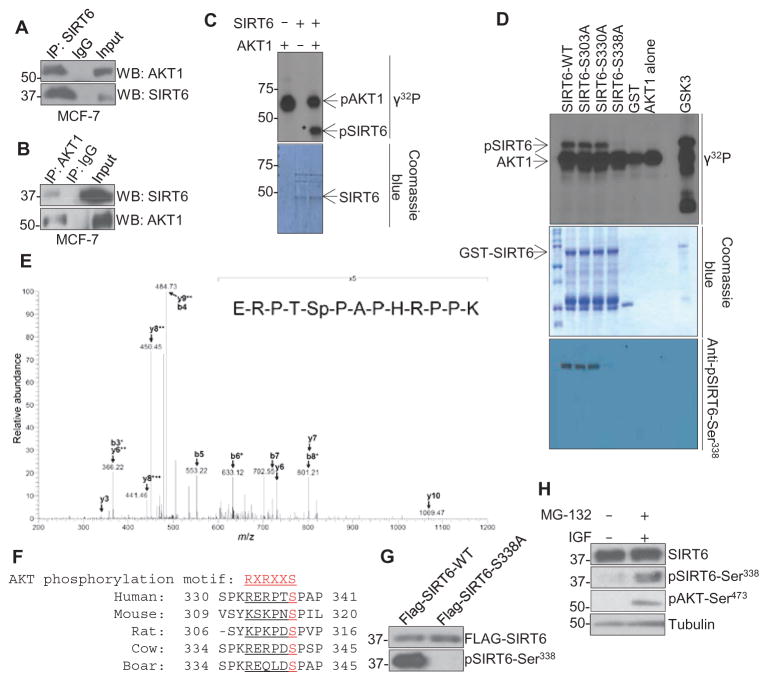
Fig. 2. AKT1 interacts with and phosphorylates SIRT6 in vitro and in vivo.
(A and B) Immunoprecipitation (IP) for SIRT6 (A) or AKT1 (B) followed by immunoblotting in lysates from MCF-7 cells against an IgG (immunoglobulin G) control. (C and D) In vitro kinase assay with recombinant, active AKT1 and either (C) recombinant GST-tagged, full-length WT SIRT6 or (D) WT or mutant SIRT6. pSIRT6, phosphorylated SIRT6; GSK3, control AKT substrate. (E) Mass spectrometry analysis of lysates from HeLa cells that had been serum-starved overnight, stimulated with EGF (50 ng/ml) for 30 min, and subjected to immunoprecipitation with a SIRT6 antibody. Spectrum is representative of two experiments. (F) Sequence alignment of the AKT1 phosphorylation motif of SIRT6 from various species. (G) Immunoblot for phosphorylated SIRT6-Ser338 (pSIRT6-Ser338) in MDA-MB-231 cells that stably express Flag-tagged WT or mutant (S338A) SIRT6, demonstrating specificity of the antibody. (H) Western blots for phosphorylated SIRT6 or AKT in lysates from MDA-MB-231 cells serum-starved overnight and then treated with IGF-1 in the presence of MG-132. Blots are representative of three experiments.