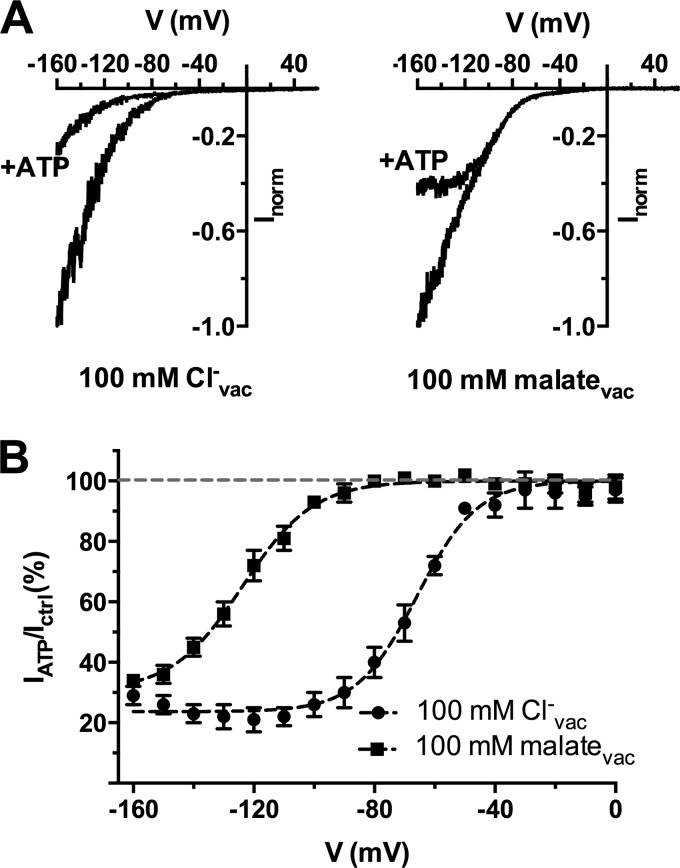
FIGURE 3.
Vacuolar anions affect the ATP-dependent block of AtALMT9-mediated chloride currents. A, normalized AtLMT9-mediated currents elicited by a voltage ramp from +60 to −160 mV in 1. 5 s (holding potential +60 mV) with a chloride-based cytosolic buffer in the presence (+ATP) or absence of 1 mm ATPfree. The vacuolar buffers contained 100 mm Cl− (left panel; 100 mm Clcyt− + 1 mm malatecyt, 100 mm Clvac−) or malate (right panel;100 mm Clcyt− + 1 mm malatecyt, 100 mm malatevac). B, fraction of unblocked current (IATP/Ictrl; mean ± S.E., n = 4) plotted against the applied membrane potential in the presence of 100 mm Cl− or 100 mm malate in the vacuolar buffer. Data were fitted with Equation 3 (“Experimental Procedures”; Table 1; dashed lines) yielding V½ = −66 ± 1 mV (100 mm Clvac−) and V½ = −124 ± 1 mV (100 mm malatevac). Error bars denote S.E.