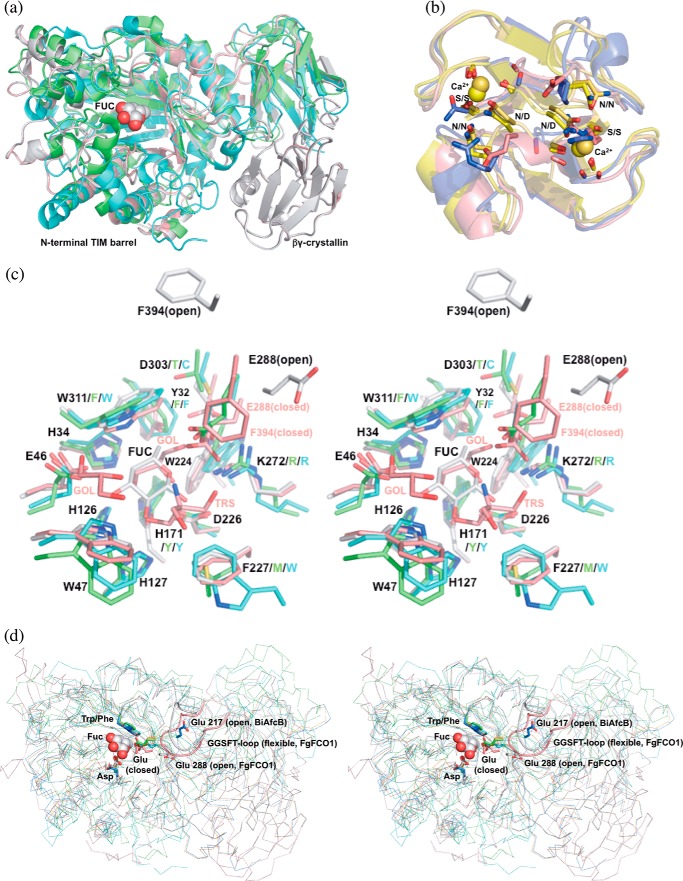
FIGURE 4.
Structure alignments of GH29 α-l-fucosidases and homologs of crystallin domains. a, FgFCO1 (white, open; pink, closed), T. maritima (green) (27), and B. thetaiotaomicron (cyan) (28) fucosidases show conserved N-terminal (β/α)8 TIM barrel and β-sandwich domains and a non-conserved crystallin domain in FgFCO1. Fucose bound in FgFCO1 is shown as spheres. b, crystallin domains of FgFCO1 (pink) and human eye γS-crystallin (blue) (70) differ from M. xanthus Protein S (yellow) (68), and an F. johnsoniae GH64 enzyme (gold) (69). The calcium binding motif (N/D)(N/D)XX(T/S) is conserved in the crystallin domains of M. xanthus Protein S and an F. johnsoniae GH64 enzyme but not FgFCO1 or human eye γS-crystallin. Calcium ions are shown as spheres. c, stereo view of the active sites of fucosidases. Amino acid residues near active sites are labeled with the one-letter code and the residue number for FgFCO1 (after which are non-conserved residues of T. maritima and B. thetaiotaomicron enzymes). d, stereo view of backbones (ribbon) and conserved general acid/base Glu of fucosidases. Structures are aligned based on conserved nucleophile Asp and hydrophobic residue Trp/Phe (sticks), the latter interacting with C4, C5, and C6 of fucose (spheres). Non-conserved long GGSFT-loops of FgFCO1 (open and closed) are highlighted as a schematic. Two conformations of α1,3/4-l-fucosidase BiAfcB involving general acid/base Glu from B. longum subsp. Infantis (blue, open; orange, closed) are also shown in d (19, 23). FUC, l-fucose; GOL, glycerol; TRS, Tris. Structures were aligned by PyMOL (a, c, and d) or PDBeFold (b).