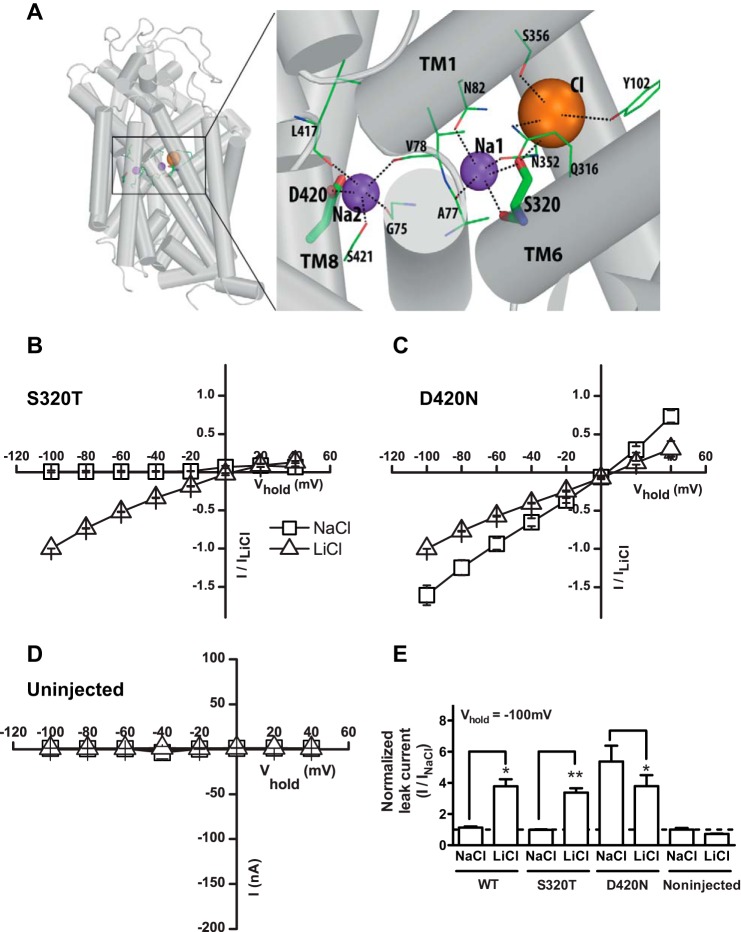
FIGURE 4.
Mutation of the second sodium site changes the selectivity of the leak current. A, model of DAT based on the structure of Drosophila DAT illustrating the involvement of Ser-320 in coordinating Na+ binding to Na1 and of Asp-420 in coordinating Na+ binding to Na2. Note that Ser-320 also is involved in coordination of Cl−. B, cocaine-sensitive leak currents in S320T shown as I/V plot of steady-state currents in NaCl (squares) and in LiCl (triangles) (means ± S.E. n = 5). The properties are similar to WT. C, cocaine-sensitive leak currents in D420N shown as I/V plot of steady-state currents in NaCl (squares) and in LiCl (triangles) (means ± S.E., n = 5). D, cocaine-sensitive leak currents in uninjected oocytes shown as I/V plot of steady-state currents in NaCl (squares) and in LiCl (triangles) (means ± S.E., n = 5). The mutation (D420N) preserved the leak in LiCl but dramatically increased the leak observed in NaCl. E, quantified cocaine-sensitive leak currents in WT, S320T, and D420N at a holding potential of −100 mV. Data are normalized to the current in Na+ (means ± S.E., n = 4–5).