FIGURE 5.
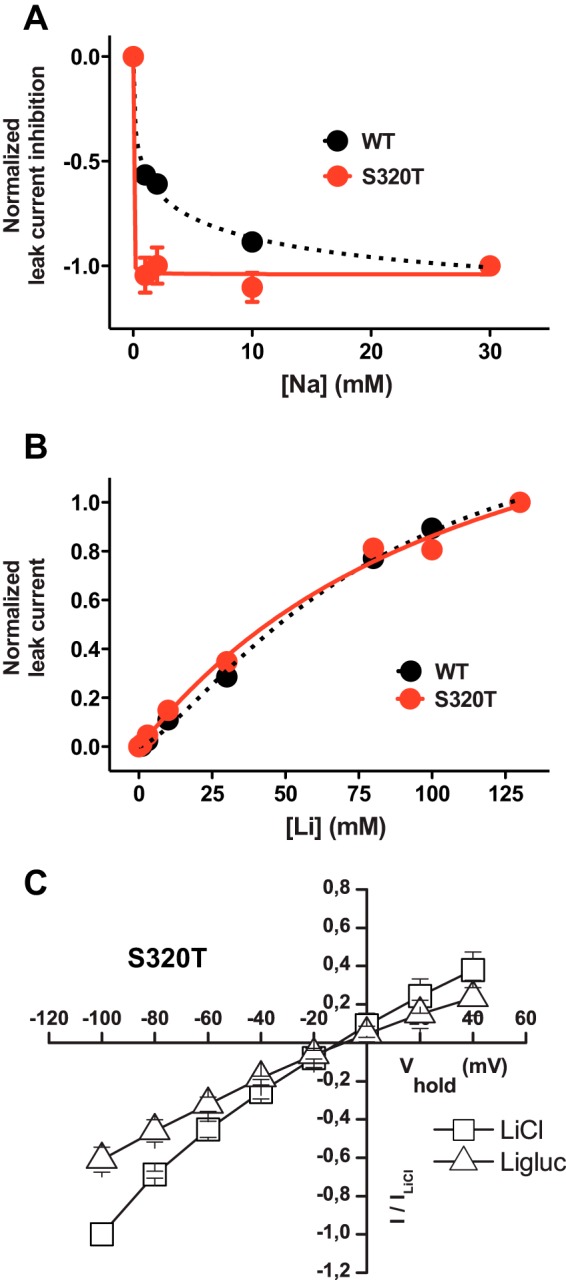
Mutation of the first sodium site changes affinity for Na+ but not Li+. A, inhibition in WT (black circles/dotted line) and S320T (red circles/solid line) of the leak current by Na+ at −100 mV plotted against increasing Na+ concentrations after normalization to the maximum inhibition (means ± S.E., n = 3–4). Mutation of the Na1 site (S320T) dramatically increased the affinity for Na+ as evaluated by the ability of Na+ to inhibit the Li+ leak with full inhibition observed at concentrations ∼1 mm. B, Li+ dose-response curves for WT (black circles/dotted line) and S320T (red circles/solid line). The currents were normalized to the maximum Li+ current and plotted against increasing Li+ concentrations. ChCl was isotonically substituted with LiCl. EC50 was 111 ± 36 mm for WT and 81 ± 13 mm for S320T (means ± S.E., n = 3–4). C, I/V plot of steady-state leak currents in S320T in LiCl and Ligluc (means ± S.E., n = 4) showing that Cl− gates the Li+ current in S320T similar to our findings for the WT. The I/V plot was generated in 20-mV steps from −100 to +40 mV.
