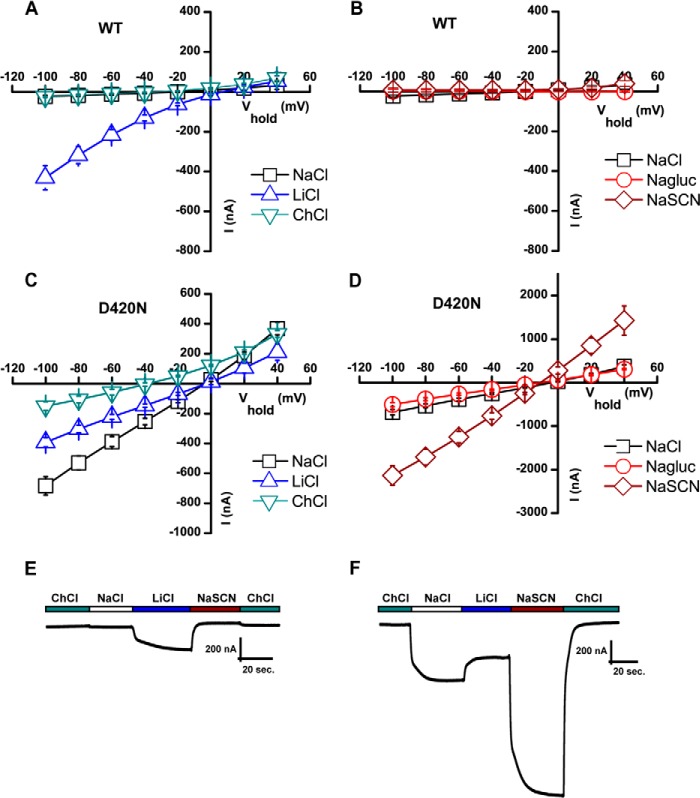
FIGURE 7.
Mutation of the Na2 site changes cation selectivity of the leak. A and C, I/V plot of steady-state cocaine-sensitive leak currents in WT (A) and D420N (C) assessed in NaCl (open black squares), LiCl (open blue triangles), and ChCl (open green triangles) (means ± S.E., n = 3–4). A large leak current was seen in NaCl for D420N but not for the WT. When Na+ was removed from the extracellular side by changing from NaCl to ChCl, a change in reversal potential was observed for D420N in agreement with Na+ being the principal permeating ion. B and D, I/V plot of steady-state cocaine-sensitive leak currents in WT (B) and D420N (D) assessed in NaCl (open black squares), sodium gluconate (Nagluc; open red circles) and NaSCN (open brown diamonds) (means ± S.E., n = 3–4). E and F, trace recordings of WT and D420N clamped at −60 mV, illustrating the effect of substituting with thiocyanate (SCN). Buffer changes were made as indicated. The figure shows representative traces.