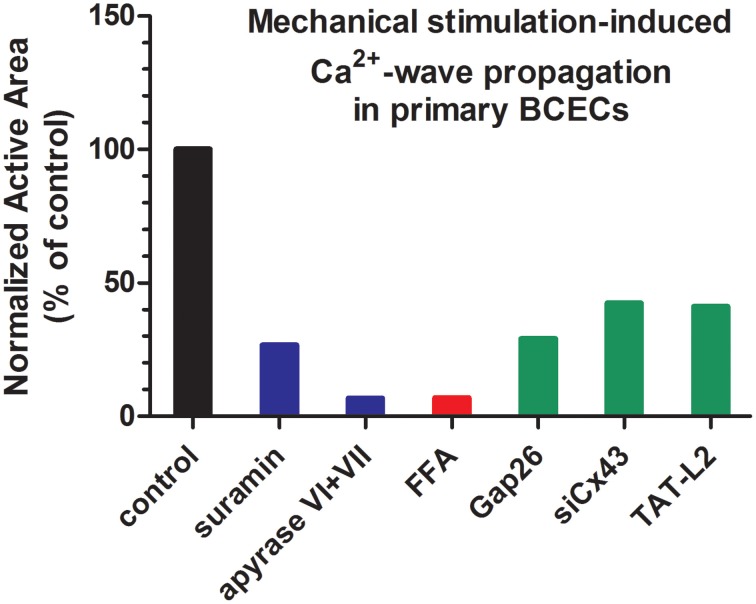
Figure 3.
Characteristics of intercellular communication in BCECs. A graph depicting the characteristics of intercellular communication in BCECs, based on mechanical stimulation-induced Ca2+-wave propagation data (active area) previously published in (Gomes et al., 2005a,b; Ponsaerts et al., 2010b). Data were further normalized to their respective controls (set at 100%). The graph is intended to indicate the relevance of ATP release (blue bars), hemichannels (red bar) and Cx43-based hemichannels (green bars). In general, the data indicate that mechanical stimulation-induced Ca2+ wave propagation is almost completely driven by release of ATP into the extracellular environment (~90% inhibition by ATP-degrading enzymes) and that Cx43 hemichannels are a major release pathway for this ATP (~60% inhibition upon Cx43 knockdown or inhibition), although other Cx and/or Panx isoforms likely contribute to ATP release. Since this graph is intended to provide a general view, readers should access the original research paper for obtaining information about the mean data and their respective SEM values.