Fig. 1.
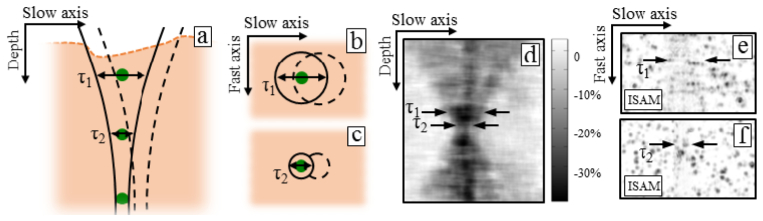
A graphical depiction and experimental validation of the interrogation time. (a-c) As the Gaussian beam performs a raster scan in a telecentric setup, particles further from the focus see a longer interrogation time (the length of which is indicated by τ) than particles at the focus. This means that stability is required over a longer period of time further from focus. (d-f) Experimentally, a short, impulse-like disturbance to the sample results in a degradation of the ISAM reconstruction. (d) Points in the sample being interrogated during the disturbance will not be reconstructed properly leading to a higher loss in contrast (black) while points not being interrogated experience little to no loss in contrast (white). (e) An en face plane away from the focus experiences signal degradation over a large area (indicated by black arrows), while an en face near the focus (f) is disrupted over only a small area (indicated by black arrows).
