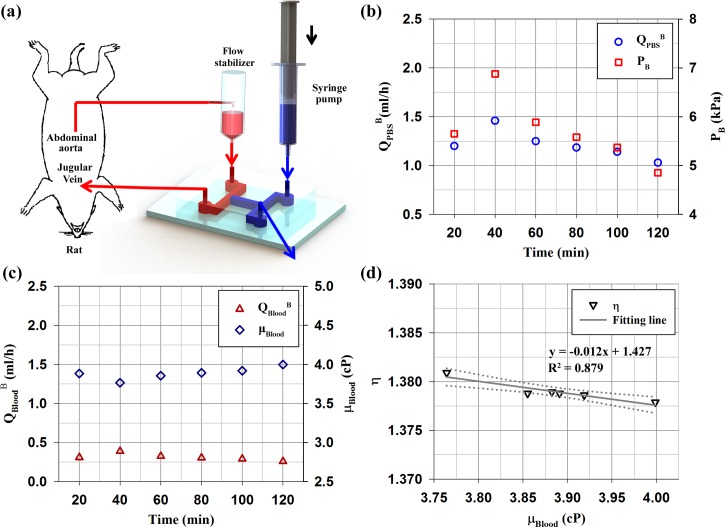
FIG. 5.
(a) Schematic of the microfluidic device for monitoring the temporal variations of biophysical properties of rat blood circulating in a complex fluidic network. The fluidic network is established by connecting the abdominal aorta and jugular vein in an extracorporeal rat bypass model. The extracorporeal rat bypass loop consists of a flow stabilizer (air cavity = 0.5 ml) and microfluidic channel. To measure biophysical properties (viscosity, flow rate, pressure), PBS solution is supplied as a reference fluid by using a syringe pump. (b) Temporal variations of the flow rate of PBS solution at the hydrodynamic balancing state (QPBSB) and the balancing pressure (PB) of rat blood circulating within the complex fluidic network. (c) Temporal variations of flow rate of blood at the hydrodynamic balancing state (QBloodB) and rat blood viscosity (μBlood) measured by using Eq. (1). (d) Relationship between the velocity ratio (η) and blood viscosity (μBlood). Solid line depicts the linear-curve fitting with respect to blood viscosity. R2 values and the corresponding fitting equations are included. Dotted lines indicate 95% confidence intervals.