Figure 1.
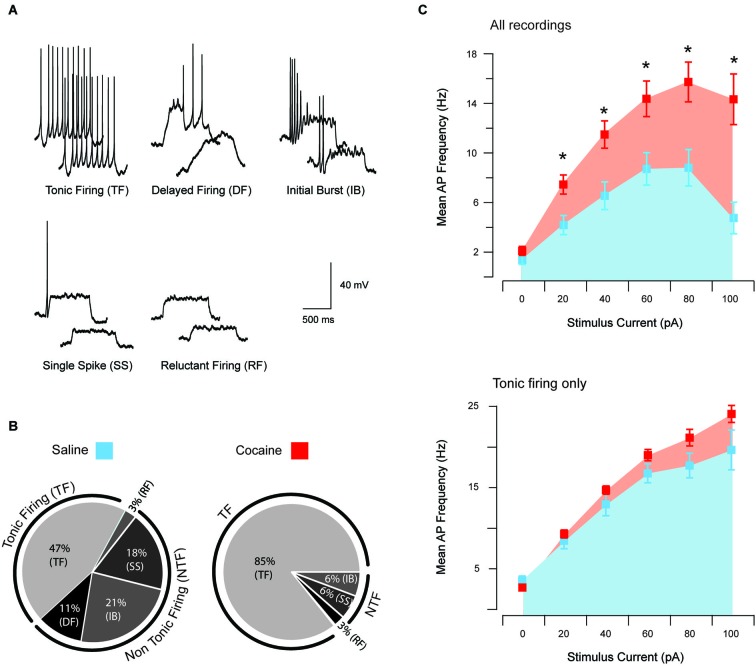
Action potential discharge and current-discharge frequency of anterior PVT neurons. Five distinct patterns of AP discharge were observed in aPVT neurons during response to current step injections of increasing amplitude; tonic firing (TF), delayed firing (DF), initial burst (IB), single spike (SS), and reluctant firing (RF) (A). All five AP firing patterns were observed in recordings from saline-exposed animals, with 44% exhibiting TF, 11% DF, 24% IB, 18% SS and 3% RF (B, left). In contrast, cocaine-exposed animals only showed four of the five described AP firing patterns, with 85% exhibiting TF, 3% RF, 6% SS and 6% IB (B, right). A chi-squared analysis revealed a significant interaction between cocaine treatment and firing pattern type, χ2 (4, n = 73) = 13.53, p = 0.009. Recordings from cocaine-exposed animals reached higher mean AP discharge frequency at all current step injections above 20 pA (C, upper). In contrast, the same comparison of AP discharge frequency, specifically in tonic firing PVT neurons from both treatment groups, did not differ (C, lower).