Table 1.
Summary of H2S donors.
| H2S donors | Structures | H2S release mechanism |
Representative bioactivities |
Key ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2S (gas) | H2S | Authentic H2S resource | Hibernation induction Type II diabetes amelioration | 67–70 |
| Sulfide salts | NaHS & Na2S | Hydrolysis | Heart failure reduction Anti-inflammation | 75–83 |
| Garlic-derived sulfur compounds | R-S-Sn-S-R | Thiol activation | Vasodilation | 86 |
| Lawesson’s reagent |
|
Hydrolysis | Anti-inflammation Ion channel regulation | 97, 98 |
| GYY4137 |
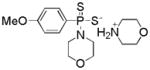
|
Hydrolysis | Vasodilation Anti-inflammation Anti-cancer | 99, 105, 106 |
| Phosphorodithioates |
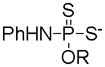
|
Hydrolysis | Prevention against oxidative damages | 107 |
| DTTs |
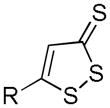
|
Hydrolysis | Anti-inflammation Anti-cancer | 114, 124–126, 129 |
| N-(acylthio)-benzamides |
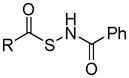
|
Thiol activation | No biological effects were reported to date. | 132 |
| S-SH compounds |
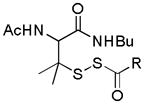
|
Thiol activation | MI/R protection | 133 |
| Dithioperoxyanhydrides |
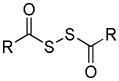
|
Thiol activation | Vasodilation | 137 |
| Arylthioamides |
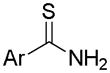
|
Thiol activation | Vasodilation | 140 |
| Gem-dithiol compounds |
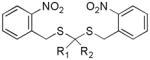
|
Light activation | No biological effects were reported to date. | 141 |
| Ketoprofenate-caged compound |
|
Light activation | No biological effects were reported to date. | 149 |
| Thioamino acids |
|
Bicarbonate activation | Vasodilation | 150 |
