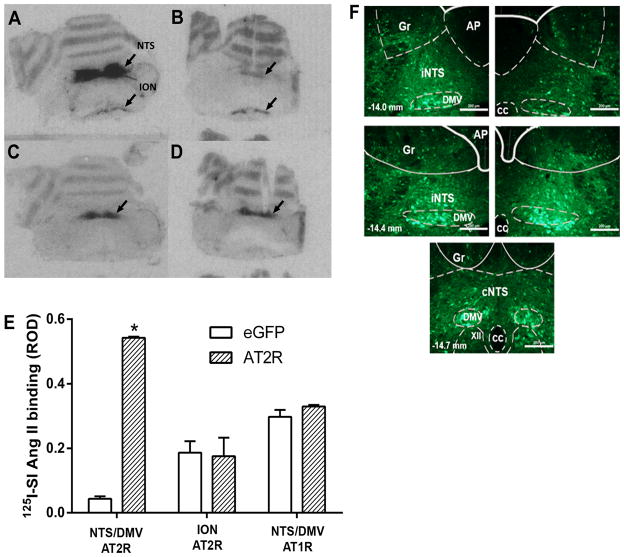
Figure 1. Viral-mediated transduction of GFP and AT2R into the brainstem.
(A–D) Receptor autoradiography of rat brainstem using 125I-SI-Angiotensin II following microinjection of AAV2-CBA-eGFP or AAV2-CBA-AT2R as described in the Methods. (A) Binding to the AT2R in a representative AT2R-transduced brain; (B) Binding to the AT2R in a representative eGFP-transduced (control) brain; (C) Binding to the AT1R in a representative AT2R-transduced brain; (D) Binding to the AT1R in a representative eGFP-transduced (control) brain. NTS, nucleus of the tractus solitarius; DMV, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; ION, inferior olivary nucleus; (E) Quantification of AT2R density in the NTS/DMV and ION and AT1R density in the NTS/DMV of AT2R or eGFP transduced rats. ROD, relative optical density. Data are means + SEM; n = 3/group; *p < 0.05 vs. corresponding eGFP group; (F) Representative fluorescence micrographs taken from coronal sections of the NTS/DMV (−14.0 to −14.7 mm from bregma) from rats that had received microinjections of AAV2-CBA-eGFP as described in the Methods. iNTSi: intermediate nucleus of the solitary tract; cNTS: commissural nucleus of the solitary tract; AP: area postrema, DMV: dorsal motor nucleus of vagus; XII: hypoglossal nucleus; Gr: gracile nucleus; cc: central canal. Scale bar: 200 μm.