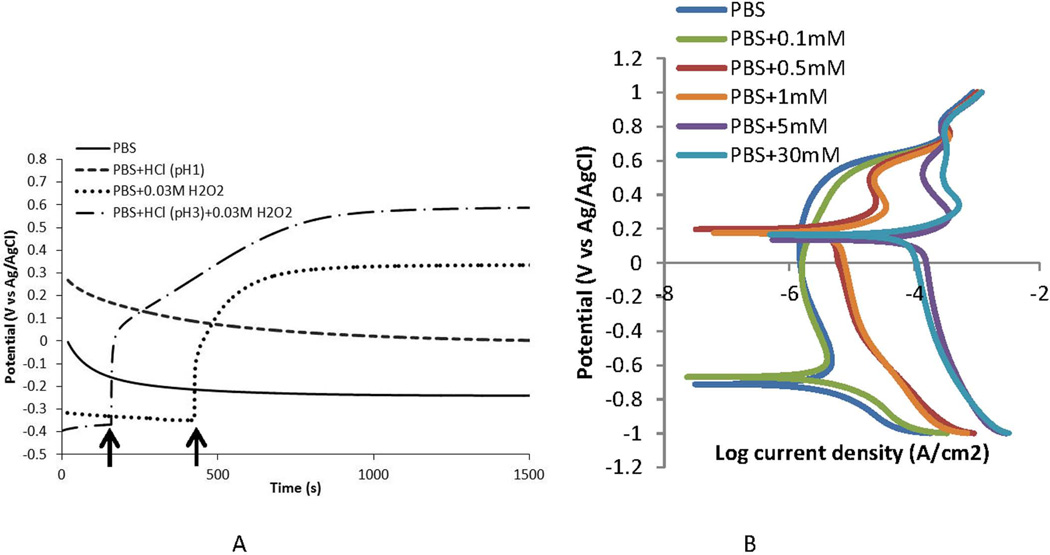
Figure 9.
A) Open circuit potential plots of CoCrMo in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4, room temperature) and in solutions modified with HCl (pH 1 and 3) and H2O2 (0.03M). OCP was raised above PBS levels to a higher oxidizing potential when acid alone, or H2O2 alone were added to the PBS solution (see arrows). When both acid and H2O2 are added to PBS, the OCP rises to above 0.6 V vs Ag/AgCl which is a highly oxidizing condition for CoCrMo. B) Polarization plots of CoCrMo in PBS solutions with differing amount of H2O2. As H2O2 concentration increases from 0.1 mM to up to 30 mM, the corrosion currents rise significantly above the PBS alone and the corrosion potential shifts positively to 0.2 V.