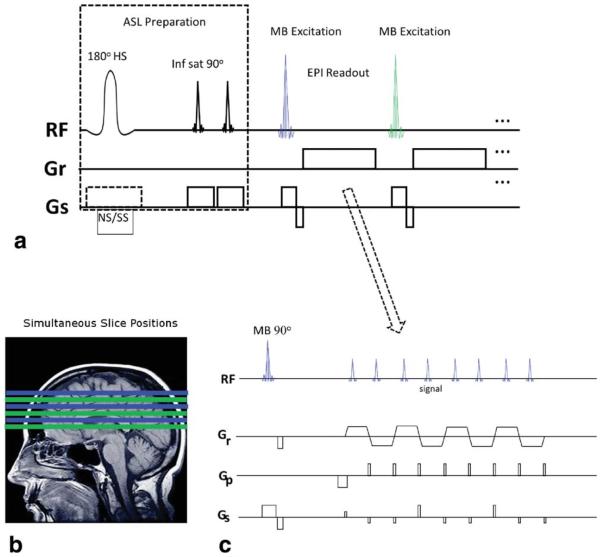
FIG. 1.
Diagram of SMS-EPI ASL pulse sequence. a: the initial ASL preparation of the sequence (left) uses nonselective and slab selective (NS/SS) inversion pulses in consecutive TRs, and QUIPSSII saturation in regions inferior to the image volume. The image readout (right) is similar to conventional multi-slice 2D EPI using multibanded (MB) excitation pulses to reduce the number of echo trains. More slices may be readout within a time window than possible with 2D EPI. b: Slice positioning with MB-3. Each MB pulse and echo train creates three slices (same color) which are widely separated to improve slice unaliasing. c: SMS-EPI echo train with blipped-CAIPI gradient pulses on Gs slice axis for controlled aliasing.