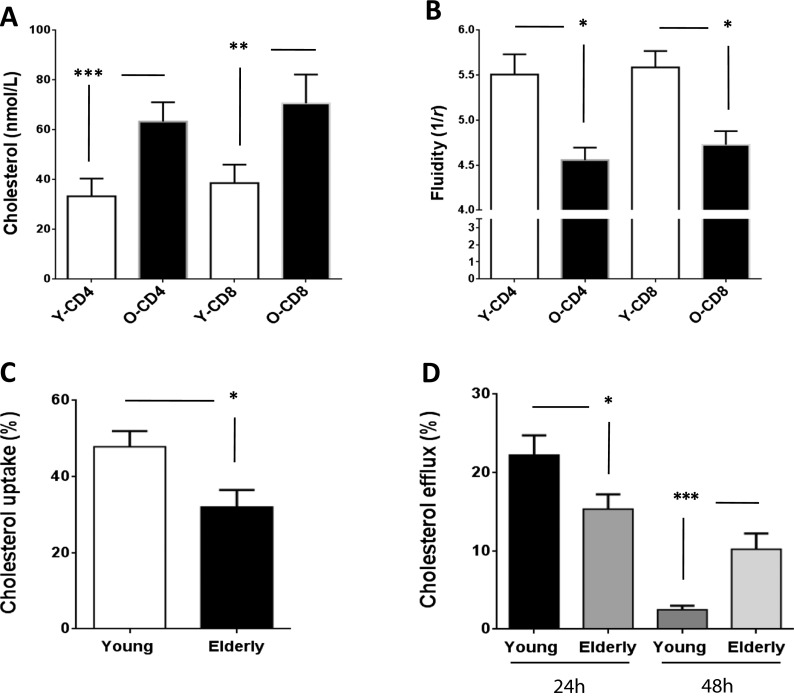
Fig. 1.
Age-related alterations in T cell membrane cholesterol exchange. The cholesterol content (a) as well as the fluidity (b) of T cells from young (white bars) and elderly individuals (black bars) is shown. Significant difference is displayed with ***p < 0.0001 and **p < 0.001. The ability of T cells to uptake and release cholesterol at steady state was tested by using radiolabeled cholesterol. T cells from young individuals were able to better uptake cholesterol from the extracellular milieu (c, *p < 0.05) and also to release it faster (24 h) that T cells from elderly individuals (d, *p < 0.05). Cholesterol efflux (radiolabeled cholesterol released from cells) was calculated using the following formula: (radioactivity (cpm) in supernatant / radioactivity (cpm) in cells + medium) × 100. The cholesterol influx was measured by determining the percentage of radiolabeled cholesterol incorporated (% cholesterol influx) using the following formula: (cpm in the cell / cpm in the cell + medium) × 100