Table 3.
Examples of plant derivatives and their antimicrobial activities
| Plant-derived antimicrobial groups | Structure | Chemical properties | Effective on microbes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinones |
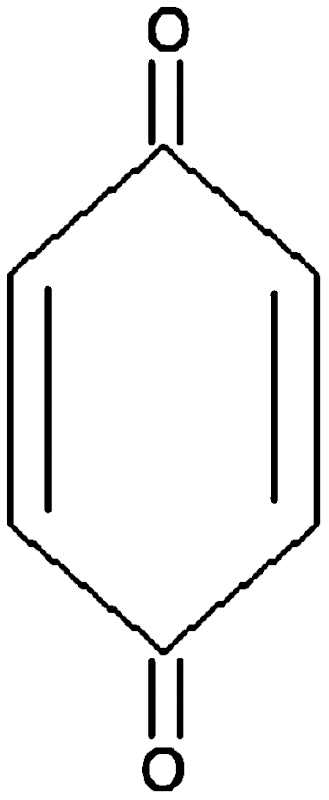
|
Conjugated cyclic-dione structure with molecular formula C6H4O2 e.g. Anthraquinone from Cassia italica | Pseudomonas pseudomallei, Bacillus anthracis, Corynebacterium pseudodiphthericum, Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Kazmi et al. (1994) |
| 6-(4,7 Dihydroxy-heptyl)quinone | Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Proteus vulgaris | Ignacimuthu et al. (2009) | ||
| Alkaloids |
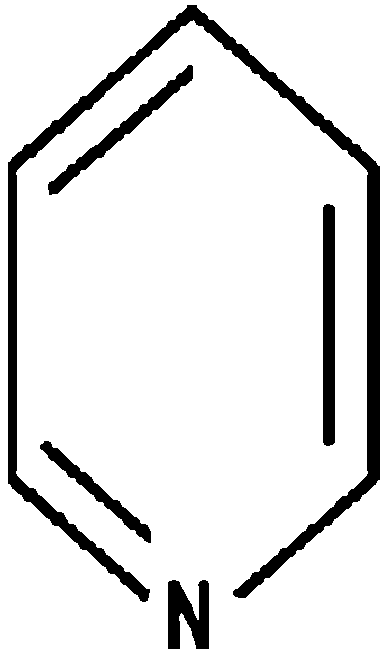
|
Naturally occurring amines having nitrogen in heterocyclic ring of compounds and are the derivative amino acids e.g. glabradine from tubers of Stephania glabra | S. aureus, S. mutans, Microsporum gypseum, M. canis, Trichophyton rubrum | Semwal and Rawat (2009) |
| l-Proline derived Monophyllidin from Zanthoxylum monophyllum | Enterococcus faecalis | Patino and Cuca (2011) | ||
| Lectins and polypeptides | – | Lectins are carbohydrate binding proteins (phytoaglutinin) with MW around 17,000–400,000 | E. coli, P. aeruginosa, Enterococcus hirae, Candida albicans (fungi) | (Zhang and Lewis (1997) |
| Flavones/flavonoids/flavonols |
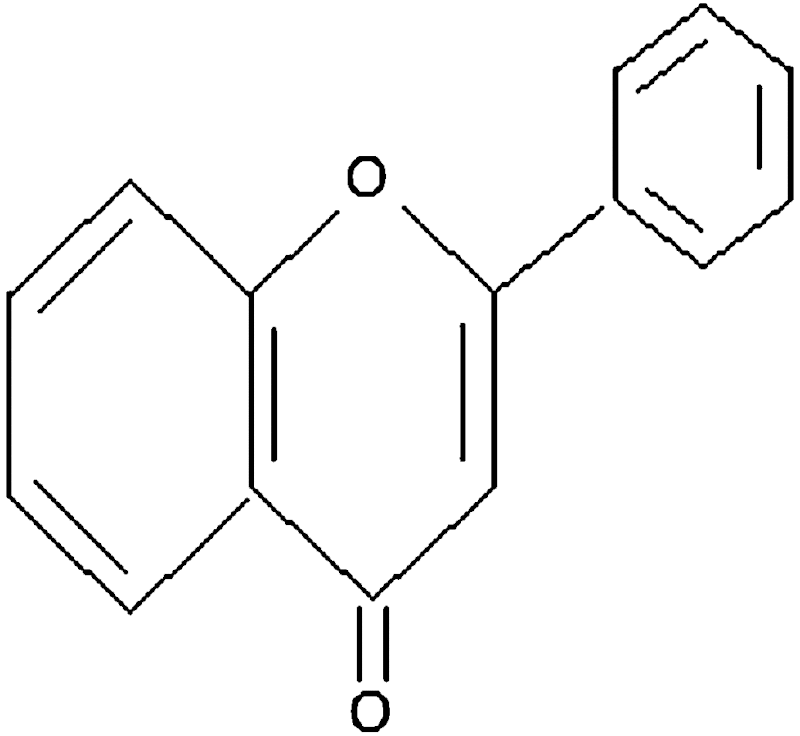
|
Are ubiquitous in plant’s parts, fruits, seeds, flowers and even honey. Flavones are hydroxylated phenolics containing one carbonyl group | MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, E. coli | Özçelik et al. (2008); Edziri et al. (2012) |
| Coumarins |
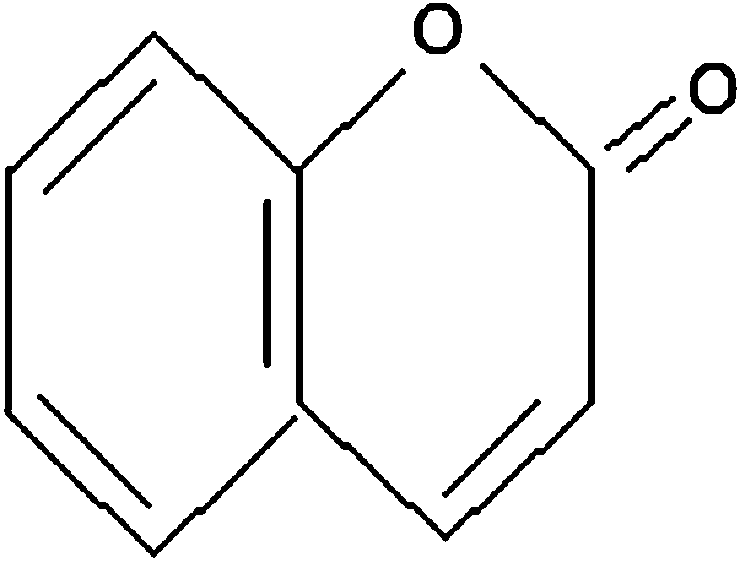
|
Coumarins are phenolic substances made of fused benzene and alpha pyrone ring forming toxic compounds found in plants such as Dipteryx odorata, Anthoxanthum odoratum etc | S. mutans, S. viridans, S. aureus | Widelski et al. (2009); Lewis and Ausubel (2006) |
| Terpenoids and essential oils |
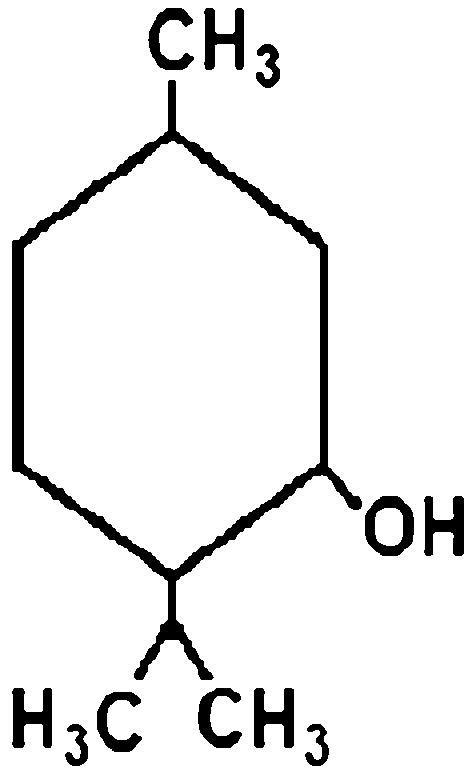
|
Isoprene derivatives having a general formula C10H16 therefore also called as Isoprenoids. Well-known examples include menthol | S. viridans, S. aureus, E. coli, B. subtilis, Shigella sonnei (highly active) P. aeruginosa, E. coli, S. aureus, T. mentagrophytes (low activity) | Banso (2009); Ragasa et al. (2008) |
| Tannins |
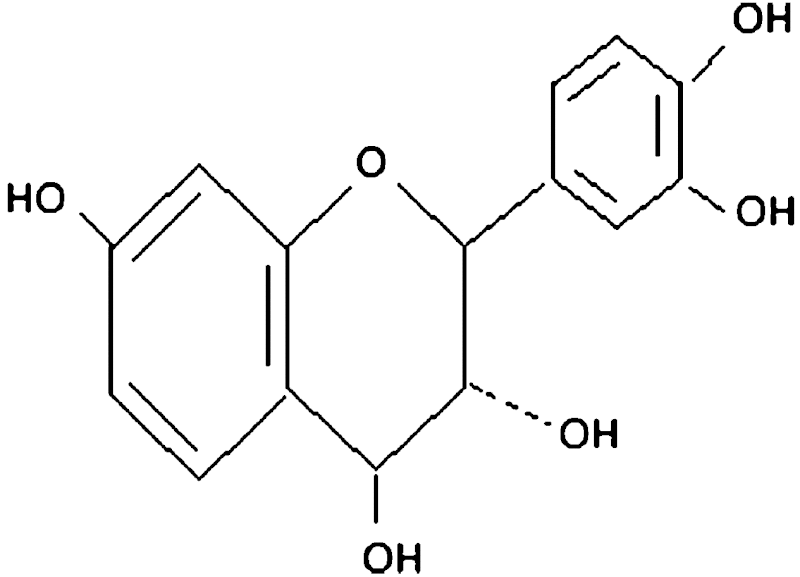
|
Large polyphenolic compound containing sufficient hydroxyls and other suitable groups | S. aureus, S. typhimurium, | Moneim et al. (2007) |
Chemical structure given in front of corresponding group of antimicrobials is not to be considered as generalized one, the references are in correspondence with bacteria
