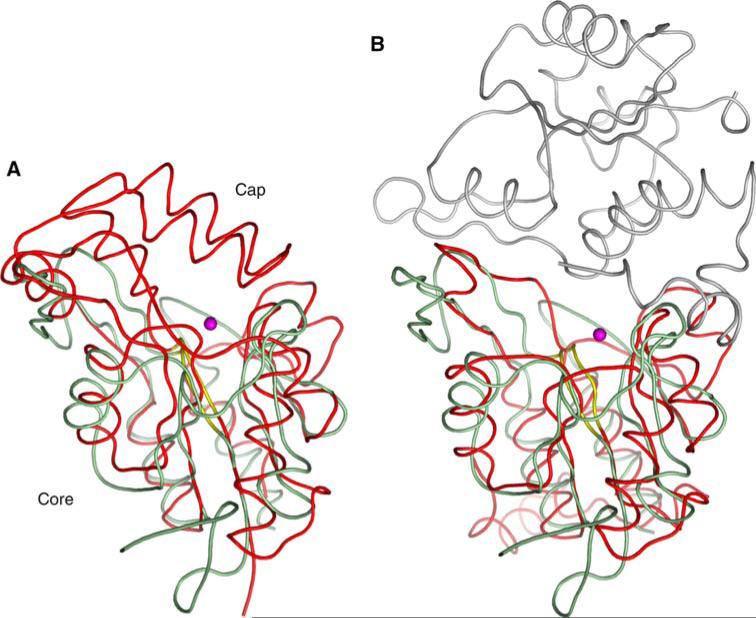
Fig. 8.
Structural comparisons of SCP3. (a) Superposition of SCP3 (green) with Methanococcus jannaschii phosphoserine phosphatase (red, PDB ID: 1F5S). The SCP3 catalytic site is freely accessible to solvent, whereas the alpha-helical capping domain in phosphoserine phosphatase shields its active site. (b) Superposition of SCP3 (green) with a dimer of the tetrameric Haemophilus influenzae deoxy-d-mannose-oculosonate 8-phosphatase (red and grey, PDB ID: 1K1E). Mg2+ ions are shown as pink spheres, and conserved phosphate-binding loops are shown in yellow. The capping domain of 1F5S occludes the active site entrance. In 1K1E, the second subunit of the dimer plays a similar role