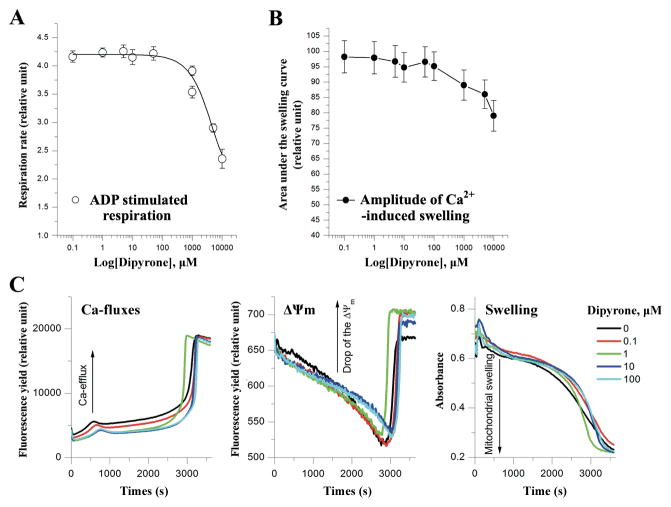
Figure 1.
Dipyrone does not affect normal mitochondrial functions in isolated mitochondria. A, Dipyrone did not significantly alter mitochondrial respiration in the isolated mitochondria over a range of concentrations from 0.1 to 1000 μM. ADP stimulated mitochondrial state 3 respiration rate was determined using the oxygen sensitive fluorescent dye A65-N1 with isolated rat liver mitochondria (0.5mg/ml). Values are presented as mean ± S.E.M. (n=5). B, Dipyrone did not affect Ca2+-induced mPT in the isolated mitochondria over a range of concentrations from 0.1 to 1000 μM. Mitochondrial mPT was assessed by swelling amplitude with the determination of light scattering changes. Values are presented as mean ± S.E.M. (n=5). C, Typical multi-parameter measurements of the Ca2+-induced mPT in the presence of dipyrone at 0 to 100 μM. “Ca-fluxes”, “ΔΨm”, and “Swelling” represent changes in extramitochondrial Ca2+ concentration, mitochondrial membrane potential, and light scattering, respectively. To induce mPT, after preincubation with dipyrone, 10 μM Ca2+ ions was added to aliquot of rat liver mitochondria (0.5mg/ml) at time point “0”. Fluorescent dyes Ca-Green-5N (0.3 μM) and TMRM (0.1 μM) were used to measure Ca-fluxes and ΔΨm, respectively. Swelling was simultaneously measured as changes of light scattering.