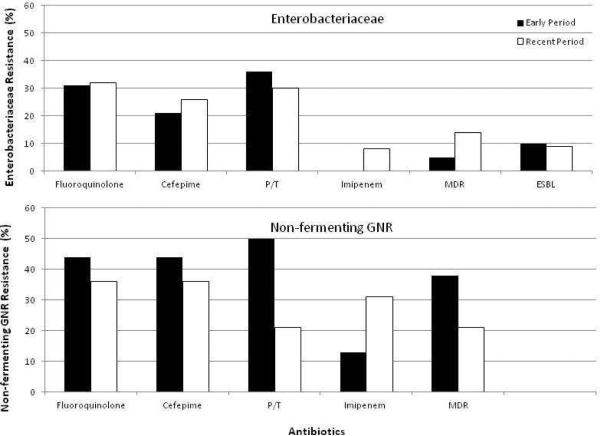
Figure 2. Rates of antimicrobial resistance in Enterobacteriaceae and non-fermenting aerobic GNR.
Y- axis: percentage of resistant isolates. Black bar: Early Period 2000-2005; Blank bar: Recent Period 2006-2011. Pairwise comparison was performed between Early and Recent period for each antibiotic, P values are not significant for all.
1Fluoroquinolone resistance denotes resistance to ciprofloxacin or/and levofloxacin
2P/T:piperacillin/tazobactam
34 ESBL in Early Period and 7 ESBL in Recent Period contributed to the resistance of Cefepime and P/T.
4Non-fermenting GNR includes only Ps. aeruginosa and Acinetobacter spp.
5MDR (Multidrug resistance) was defined as resistant to at least 2 of the following: fluoroquinolone, cefepime, piperacillin/tazobactam, or carbapenems.