Figure 6.
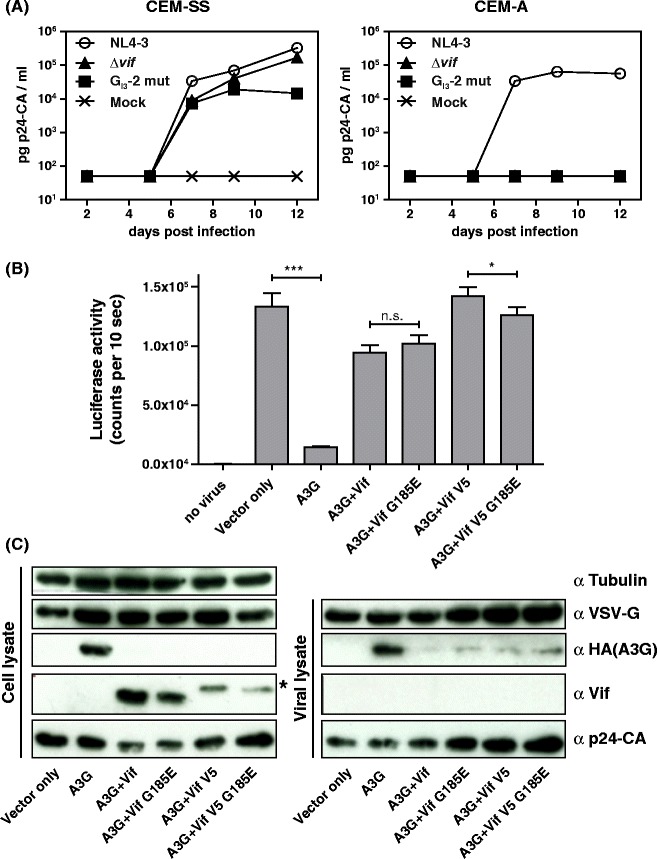
G I3 -2 is critical for efficient virus replication in A3G expressing cells. (A) CEM-SS and CEM-A cells were infected with wild type or GI3-2 mutant NL4-3 virus and virus production was determined by p24 CA capture ELISA of cell-free supernatant collected at the indicated time points. (B) Vif G185E mutant counteracts A3G with comparable efficiency as wild type Vif. Viral rescuing activity of Vif and Vif G185E mutant against A3G compared to vector only control (no A3G). HIV-1 Δvif.luc reporter viruses were generated in the presence of A3G and absence of A3G (vector control), and A3G in combination with Vif, Vif G185E, Vif-V5, and Vif-V5 G185E plasmids. Virions were normalized by RT activity. Luciferase activity was measured 48 hours post infection. Unpaired t tests were computed to determine the differences between the group of samples reached the level of statistical significance (ns, not significant; *, P 0.05 and ***, P 0.0001). (C) Viral supernatants were concentrated through a 20% sucrose cushion by ultracentrifugation. Immunoblot analysis of the expression and encapsidation of A3G in the presence and absence of Vif, Vif G185E, Vif-V5, and Vif-V5 G185E: A3G was detected by an anti (α)-HA antibody. Vif, VSV-G, and p24-CA were detected by their respective monoclonal antibodies. Tubulin served as loading control for cell lysates and p24-CA and VSV-G for viral lysates. Asterisk in the Vif blot indicates the shift in the molecular weight of V5-tagged Vif.
