Figure 3.
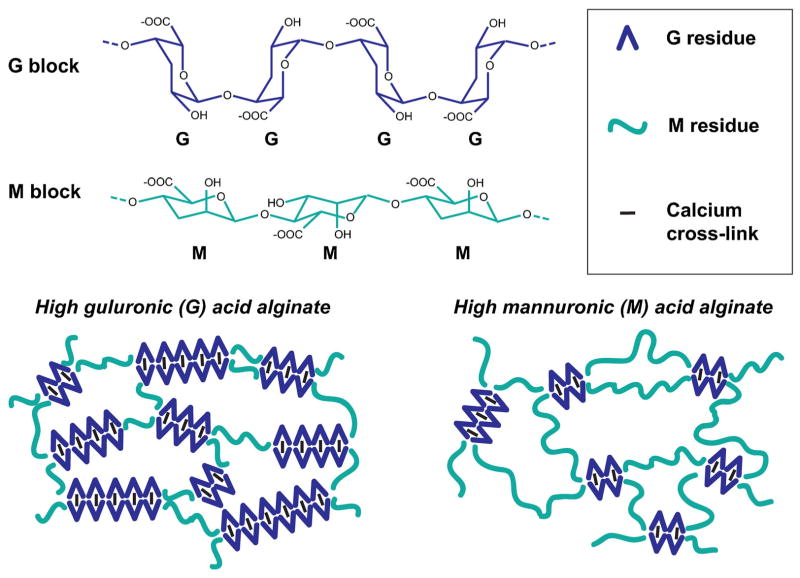
Alginate, the most common polymer used for microencapsulation, is made up of guluronic acid (G) and mannuronic acid (M) residues. The ratio of G:M residues and block lengths of each species impact the mechanics and permeability of the hydrogel material. When using calcium as the cross-linking ion, the calcium only cross-links G residues, leading to an “egg box” configuration (Simpson et al., 2004). Therefore, alginates with higher G content yield stiffer, less flexible hydrogels that maintain mechanical stability for a longer period of time.