Figure 4.
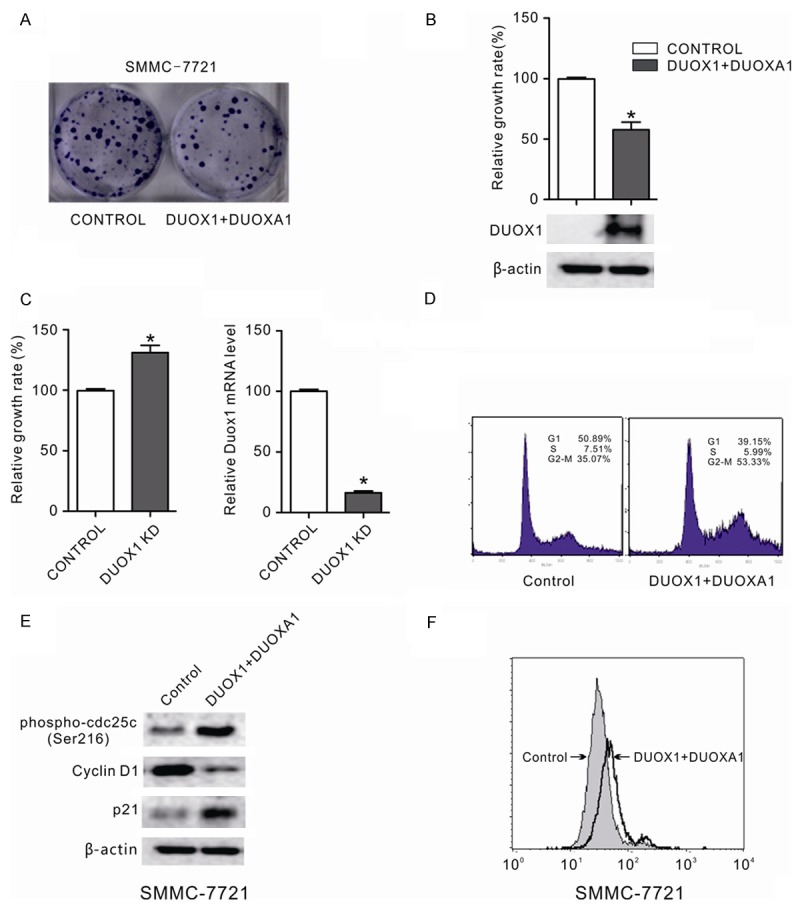
DUOX1 suppressed the growth of cancer cells by inducing G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and increasing ROS production. A: The effect of ectopic DUOX1 expression on cancer cell growth was investigated by the monolayer colony formation assay. The scanned colony formation in six-well plates was shown in the panel. B: The growth of cancer cells after DUOX1 overexpression was determined by MTS cell growth assay. Ectopic expression of DUOX1 suppressed the growth of cancer cells. DUOX1 expression level in transfected SMMC-7721 cells was confi rmed by western blot. C: Knockdown of DUOX1 promoted Hep3B cells proliferation. Hep3B cells were transfected with DUOX1 siRNA (100 nM) or NC siRNA (100 nM). After 48h, the cell growth was determined by MTS and knockdown efficiency was confirmed by real-time PCR. D: Effect of Duox1 on the cell cycle in liver cancer cell. The cell cycle distribution of liver cancer cell line SMMC-7721 with and without DUOX1 expression was evaluated by flow cytometry analysis. E: Effect of Duox1 on cell cycle regulators (phospho-cdc25 (Ser216), p21 and cyclin D1) were determined using western blotting. β-actin was used as the internal control. F: Exogenous DUOX1 increased ROS level in liver cancer cells. The effect of ectopic DUOX1 expression on oxidative stress was determined by flow cytometry assay as shown. Stable cells were stained with DCFH-DA and then the redox state of cells was measured by flow cytometry. Data are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. The gels have been run under the same experimental conditions.
