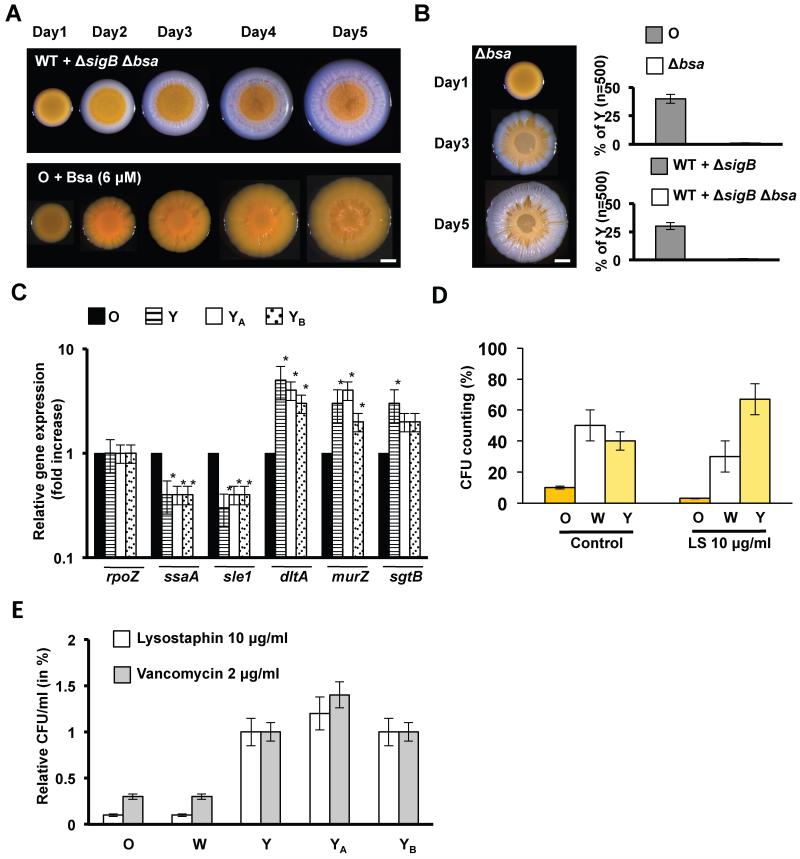
Figure 5. Y strain is a VISA-like strain.
(A) Progression of mixed LAC wild type strain + LAC ΔsigB Δbsa mutant in relation 5:1 (upper row). The communities grew in TSBMg at 37°C during 5 days. After incubation, the community failed to develop Y flares through the W sector. Progression of the O strain in TSBMg at 37°C during 5 days when supplemented with previously purified Bsa (~ 6 μM) (lower row). YB strain differentiates. Scale bar is 1mm. (B) Progression of the O strain Δbsa mutant in TSBMg at 37°C during 5 days. After incubation, the community failed to develop Y flares through the W sector. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of several VISA-related genes (ssaA, sle1, dltA murZ and sgtB) in O, Y strains and YA and YB strains derived from the artificial mixture WT+ΔsigB (fig. 3G) and Bsa supplementation (fig. 5A), respectively (Student’s t-test p ≤ 0.05). (D) Quantification of bacterial survival in response to lysostaphin treatment (LS 10 μg/ml during 15 min at 37°C). (E) Quantification of bacterial survival in response to lysostaphin and vancomycin treatment of different strains in relation to Y strain. See figs. S5, S7 and table S6.