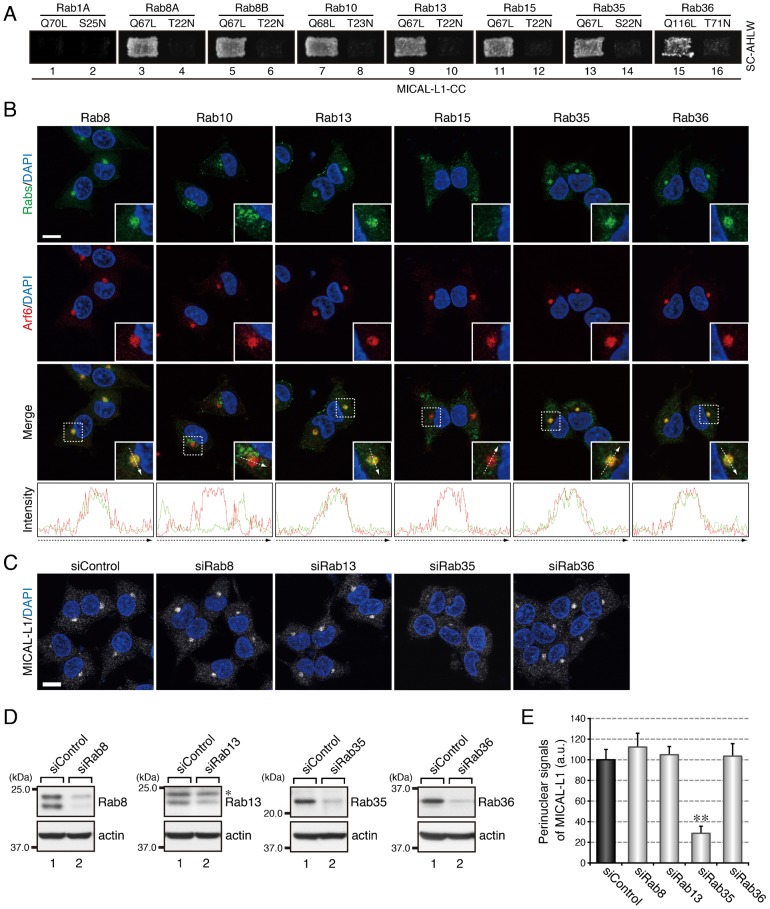
Fig. 1. Rab35 functions as a master Rab that determines the intracellular localization of MICAL-L1.
(A) Active form-dependent interaction of Rab8A, Rab8B, Rab10, Rab13, Rab15, Rab35, and Rab36 with MICAL-L1-CC. Yeast two-hybrid assays were performed to investigate whether the Rabs indicated interacted with MICAL-L1-CC. Rab1A is a negative control that does not bind MICAL-L1 at all (Fukuda et al., 2008). (B) Colocalization of Rab8, Rab13, Rab35, and Rab36 with Arf6 in PC12 cells. After stimulating PC12 cells with NGF for 6 hr, the cells were fixed and stained with the anti-Rab antibodies indicated, anti-Arf6 antibody, and DAPI. The insets are magnified views of the boxed areas. Fluorescence intensity along the broken arrows is shown at the bottom. (C) Disappearance of MICAL-L1 signals from the perinuclear area of PC12 cells after depleting them of Rab35. PC12 cells were treated with siControl, siRab8 (siRab8A + siRab8B), siRab13, siRab35, or siRab36, and after stimulating the cells with NGF for 6 hr, the cells were fixed and stained with anti-MICAL-L1 antibody and DAPI. Scale bars: 10 µm. (D) Reduced expression of Rab8, Rab13, Rab35, and Rab36 in the cell treated with siRab8, siRab13, siRab35, and siRab36, respectively. Cell lysates of PC12 cells treated with siRNAs were immunoblotted with the anti-Rab antibodies indicated and anti-actin antibody. The asterisk indicates a non-specific band of the anti-Rab13 antibody. (E) Perinuclear MICAL-L1 signals (mean and SE; arbitrary units, a.u.) of siControl-treated, siRab8-treated, siRab13-treated, siRab35-treated, and siRab36-treated PC12 cells after stimulating the cells with NGF for 6 hr (n = 60 from 3 independent experiments).