Figure 1. Biological role of AKR1D1 (A and B) and chemical structures of the steroid substrates tested.
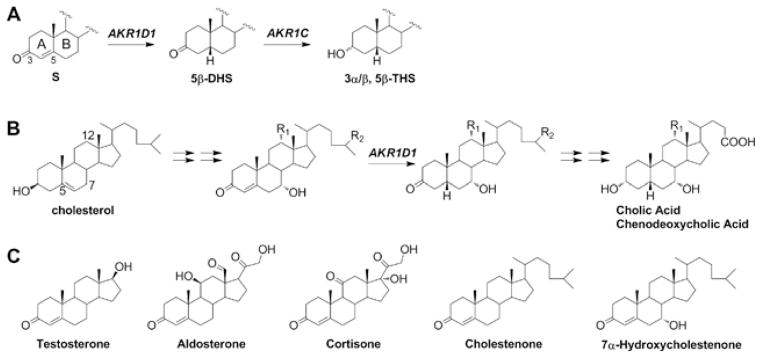
(A) Steroid hormones are metabolized by the concerted actions of AKR1D1 and AKR1C enzymes. S, steroid hormone. (B) AKR1D1 is responsible for the 5β-reduction in all pathways for the synthesis of primary bile acids cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. R1, -H or -OH; R2, -CH3 or -COOH. (C) All substrates are similar in chemical structure and have an identical A-ring, where the reaction occurs.
