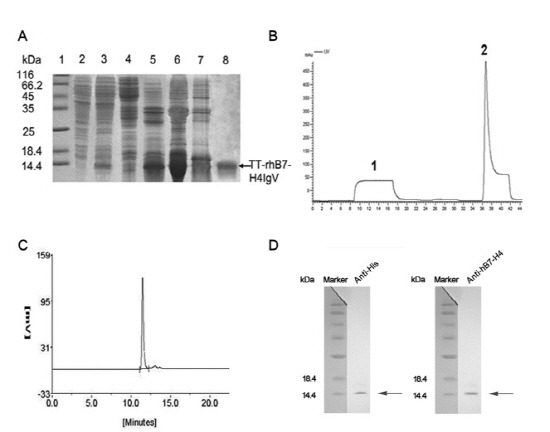
Fig. 2. Purification and identification of TT-rhB7-H4IgV. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of TT-rhB7-H4IgV expression in E. coli and purification by nickel (Ni2+) chelate affinity column. Lane 1, molecular weight standards (kDa); lane 2, total cell lysate before induction; lane 3, total cell lysate of pQE30-TT-rhB7-H4IgV after induction; lane 4, supernatant of cell lysate; lane 5, inclusion body after sonication; lane 6, inclusion body after washed with 4 mol/L urea; lane 7,8 contaminated proteins and purified TT-rhB7-H4IgV protein (corresponding to the peak1, 2 in B). (B) Elution profile of the protein by nickel (Ni2+) chelate affinity column. Peak 1, flow through; peak 2, the target protein. (C) SEC-HPLC analysis of the purity of TT-rhB7-H4IgV. 5 μg purified TT-rhB7-H4IgV were analyzed on a G2000SW column, detected at OD280. (D) Proteins were identified by Western blot with anti?his Ab (R94025, Invitrogen, USA) and anti-hB7-H4 Ab (AF1134a, ABGENT, USA). M, Protein molecular weight marker.