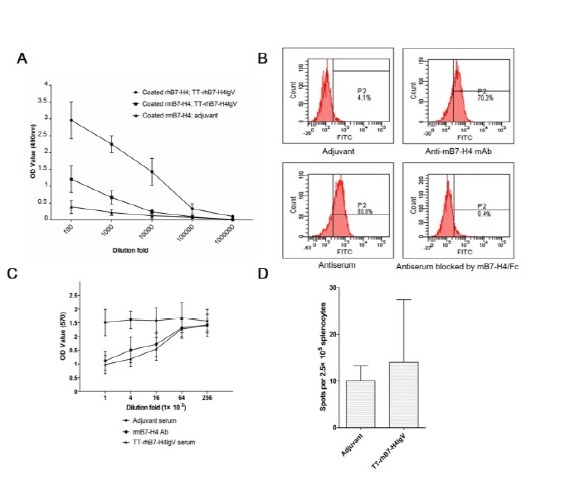
Fig. 4. (A) ELISA analysis of antiserum from mice immunized with TT-rhB7-H4IgV. Serum from mice immunized with adjuvant was used as negative control. (B) Determination of binding activity of anti-B7-H4 serum to native B7-H4 on SP2/0 cell surface by FCM. Anti-mB7-H4 mAb was used as positive control and adjuvant serum as negative control. (C) Complement-mediated cytotoxicity. Antiserum elicited by TT-rhB7-H4IgV had similar complement-mediated cytotoxicity of SP2/0 cells to anti-mB7-H4 mAb. Anti-mB7-H4 mAb was used as a positive control and the serum from adjuvant vaccination was used as a negative control. (D) Induction of B7-H4-specific IFN-γ-producing cellular immune responses by TT-rhB7-H4IgV vaccine. The number of IFN-γ-producing B7-H4-specific T cell precursors was determined using ELISPOT assay. TT-rhB7-H4IgV vaccine vs. adjuvant control P > 0.05.