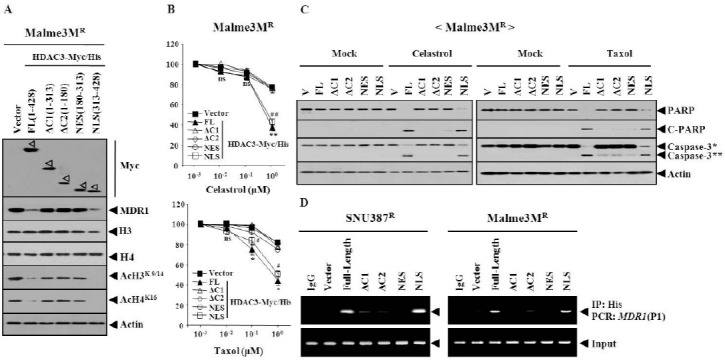
Fig. 3. The nuclear localization domain of HDAC3, which encompasses Ser424, is necessary and sufficient for conferring sensitivity to microtubule-targeting drugs. (A) HDAC3-Myc/His6 serial deletion constructs. FL denotes full-length. NES denotes nuclear export signal domain. Numbers in parentheses represent amino acid residues of HDAC3. NLS denotes nuclear localization signal domain. 48 h after transfection, Western blot was performed. (B) Malme3MR cell line was transfected with the indicated construct. The next day, cells were treated with various concentrations of the indicated drug for 24 h, followed by MTT assays. Comparison was made between SNU387R or Malme3MR cells transfected with the control vector, and the same cells transfected with HDAC3-FL. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005. Comparison was also made between SNU387R or Malme3MR cells transfected with control vector, and the same cells transfected with HDAC3-NLS. #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.005. (C) Malme3MR cell line was transfected with the indicated construct. The next day, cells were treated with celastrol (1 μM) or taxol (1 μM) for 24 h, followed by Western blot. C-PARP denotes cleaved PARP. V denotes control vector. Caspase-3* denotes pro-caspase-3 and caspase-3** denotes active caspase-3. (D) The indicated cell line was transfected with the indicated HDAC3-Myc/His construct. 48 h after transfection, ChIP assays were performed, as described. SNU387R or Malme3MR cells transfected with full-length HDAC3 were also subjected to ChIP assays, employing isotype-matched anti-IgG antibody (2 μg/ml).