Figure 3.
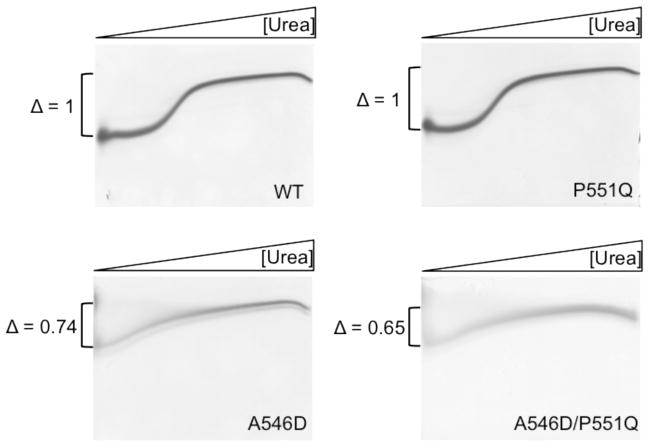
Transverse urea gradient gel electrophoresis of WT, A546D, P551Q, and A546D/P551Q recombinantly expressed FAS1-4 domains. Horizontal 0–8M urea gradient from left to right. Vertical separation based on the degree of native fold. WT and P551Q mutant FAS1-4 domains follow a classic two-state transition unfolding event whereas both the A546D and A546D/P551Q FAS1-4 domain variants follow a linear transition towards complete unfolding. Delta changes (Δ) are normalized to WT and indicates that the degree of unfolding at 0M urea is less for WT < P551Q < A546D < A546D/P551Q. The P551Q mutation alone does not contribute to FAS1-4 domain destabilization. However, in combination with the A546D mutations a destabilizing cooperative effecter is seen as the delta change is lower for A546D/P551Q than for A546D (n=2).