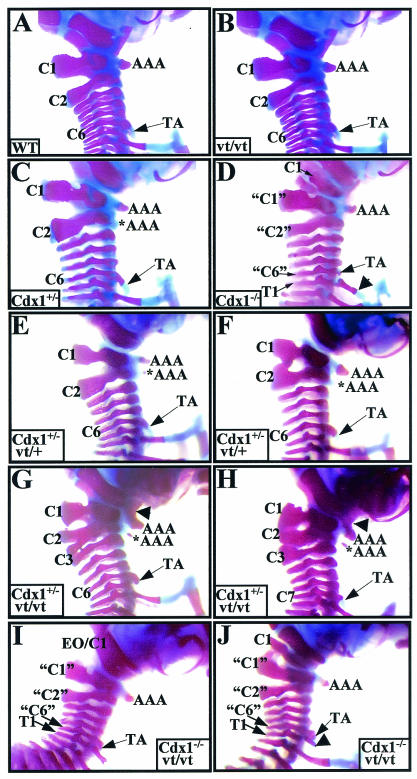
FIG. 6.
Skeletal analysis of Cdx1 Wnt3avt compound mutants. The cervical region of whole-mount skeletal preparations from (A) wild-type, (B) Wnt3avt/vt, (C) Cdx1+/−, (D) Cdx1−/−, (E and F) Cdx1+/− Wnt3avt/+, (G and H) Cdx1+/− Wnt3avt/vt and (I and J) Cdx1−/− Wnt3avt/vt offspring. Note the normal cervical region for both wild-type (A) and Wnt3avt/vt (B) mice. (C, E, and F) Cdx1+/− and Cdx1+/− Wnt3avt/+ mice exhibit similar phenotypes, notably an ectopic anterior arch of the atlas (*AAA), a broader C2 neural arch, and a C1-C2 fusion (F). (D, I, and J). Cdx1 null and Cdx1−/− Wnt3avt/vt mice exhibit identical vertebral defects, notably malformation and malposition of C1 and anterior transformation of C2, C3, and C7, denoted “C1,” “C2,” and “C6,” respectively. The arrowhead in panel J indicates a partial rib associated with presumptive T1 which does not reach the sternum. (G and H) Cdx1+/− Wnt3avt/vt offspring exhibit an exacerbated phenotype compared to either single mutant (compare panels G and H to panels B and C). In particular, note the fusion of the anterior arch of the atlas with the basioccipital bone (arrowhead) and the presence of an ectopic anterior arch of the atlas. Note also the malformations and fusions of neural arches C1 to C3 and the presence of TA on C7 instead of C6 (H). Abbreviations: AAA, anterior arch of the atlas; *AAA, ectopic anterior arch of the atlas; TA, tuberculum anterior; EO, exoccipital; C, cervical vertebrae; T, thoracic vertebrae. Quotation marks indicate presumptive anterior transformations.