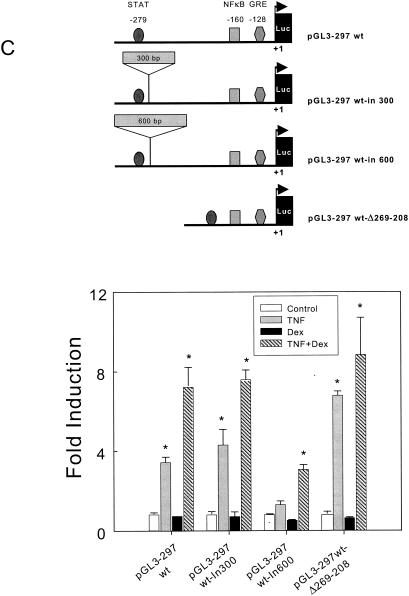
FIG. 5.
Analysis of the role of STAT transcription factor in the activation of the TLR2 promoter in A549 cells. (A) The TLR2 promoter construct pGL3-297 was used as the wild type to produce the deletion construct pGL3-297wt-Δ269-208, in which a specific deletion was conducted to remove the STAT-binding site, as indicated in Materials and Methods. The fold induction of luciferase by TNF-α, Dex, or both is shown. All samples were analyzed in duplicate, and the values are the mean ± SE of three experiments. Luciferase activities of the wild type (wt), mutated constructs, and pGL3-basic vector are shown. All samples were analyzed in duplicate, and the values are the mean ± SE of three experiments. (B) The pGL3-297wt TLR2 promoter construct was cotransfected with the STAT5b (Y699F) dominant negative expression plasmid, ramped from 0 to 5 μg. The fold induction of luciferase activities by TNF-α, Dex, or both is shown. Luciferase activities of all constructs and the pGL3-basic vector are shown. All samples were analyzed in duplicate, and the values are the mean ± SE of three experiments. (C) Interaction between NF-κB and STAT transcriptional factor binding sites during TLR2 gene transcription. A diagram of the pGL3-297 TLR2 promoter construct used as the wild type and the insertion and deletion constructs is shown (top). The shortened luciferase reporter construct pGL3-297 TLR2 was used as a template to construct pGL3-297wt-in300 and pGL3-297wt-in600 (containing a 300- and a 600-bp fragment, respectively, inserted between the NF-κB and STAT sites). The pGL3-297Δ285-269 was obtained after deletion of the DNA fragment between the NF-κB and STAT sites. The fold induction of luciferase activities by TNF-α, Dex, or both is shown. All samples were analyzed in duplicate, and the values are the mean ± SE of three experiments. *, P < 0.05 for pair comparison analysis (Tukey-Kramer test) to each control condition.