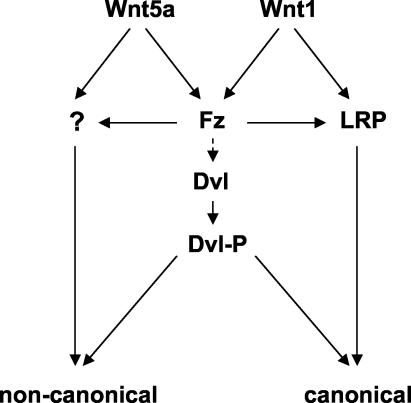
FIG. 9.
Model illustrating Dvl phosphorylation as a common response to Wnt proteins that activate distinct signaling pathways. Wnt signaling via the canonical β-catenin pathway requires both Fzd and LRP5/6, while noncanonical Wnt signaling requires Fzd and possibly additional receptors as yet uncharacterized. For simplicity, we have indicated that signals leading to phosphorylation of Dvl are derived from Fzd alone. We propose that Dvl phosphorylation is a common response to both the Wnt1 class and Wnt5a class of Wnt proteins and that it potentiates Wnt signaling via either the canonical or noncanonical pathways. Which of these pathways dominates in a given circumstance may depend on the involvement of Wnt coreceptor components in addition to Fzd and possibly on the subcellular distribution of Dvl. The reported association between different subcellular locations of Dvl protein and different signaling pathways suggests that this might be a key determinant (17).