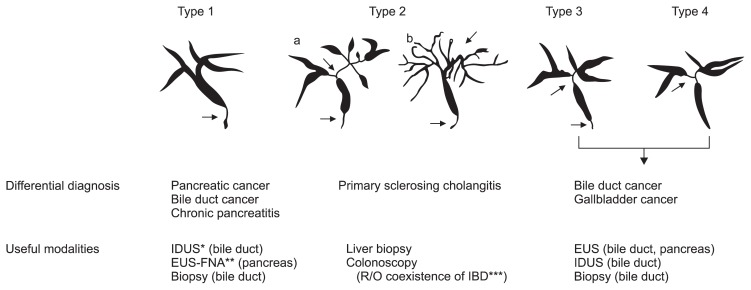
Fig. 1.
Classification of cholangiography in IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC). The characteristic features of IgG4-SC can be classified into four types, based on the regions of stricture as revealed by cholangiography and differential diagnosis. Type 1 IgG4-SC shows stenosis only in the lower part of the common bile duct, which should be differentiated from chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma. Type 2 IgG4-SC, in which stenosis is diffusely distributed throughout the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts, should be differentiated from primary sclerosing cholangitis. Type 2 is further subdivided into two types. Type 2a has a narrowing of the intrahepatic bile ducts with prestenotic dilation, and Type 2b has a narrowing of the intrahepatic bile ducts without prestenotic dilation and reduced bile duct branches, caused by marked lymphocytic and plasmacyte infiltration into the peripheral bile ducts. Type 3 IgG4-SC is characterized by stenosis in both the hilar hepatic lesions and the lower portion of the common bile duct. Type 4 IgG4-SC shows strictures of the bile duct only in the hilar hepatic lesions. Cholangiographic findings of types 3 and 4 need to be discriminated from those of cholangiocarcinoma. From Ohara H, et al. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2012;19:536–542, with permission from Springer.22
IDUS, intraductal ultrasonography; EUS, endoscopic ultrasonography; EUS-FNA, EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease.