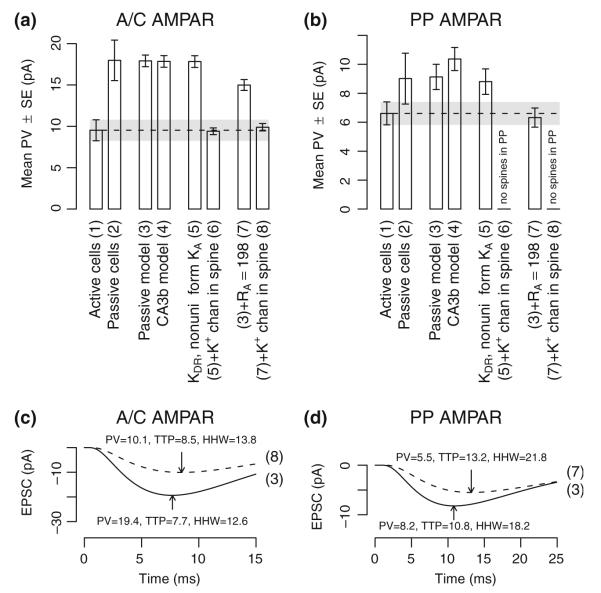
Fig. 10.
Alternative model results for non-passive AMPA receptor responses. (a) Experimental and model mean peak EPSC for A/C AMPA receptor responses. Alternative items are: (1) experimental results from active cells, i.e. where ion channels are not blocked, (2) experimental results from passive cells, i.e. where voltage-gated ion channels are blocked, (3) passive model of synaptic responses, (4) active model with ion channels from a prior study (Hemond et al. 2008), (5) passive model with KDR (gmax=10 mS cm−2) and KA (somatic gmax=20 mS cm−2) channels added such that KA conductivity scales linearly with distance from the soma, (6) previous model with an unspecified K+ channel in synaptically activated spines (gmax=1 nS), (7) passive model with Ra changed to 198 Ωcm, and (8) the previous model with an unspecified K+ channel in synaptically activated spines (gmax=0.5 nS). (b) Experimental and model mean peak EPSC for PP AMPA receptor responses. Individual items are as in panel A. Synapses in SLM are modeled without spines and items (f) and (h) are omitted for PP responses. (c) Representative EPSC traces from a single A/C AMPA receptor synapse as derived from models (3) and (8). Response peaks are indicated with arrows. (d) Representative EPSC traces from a single PP AMPA receptor synapse as derived from models (3) and (7). Response peaks are indicated with arrows