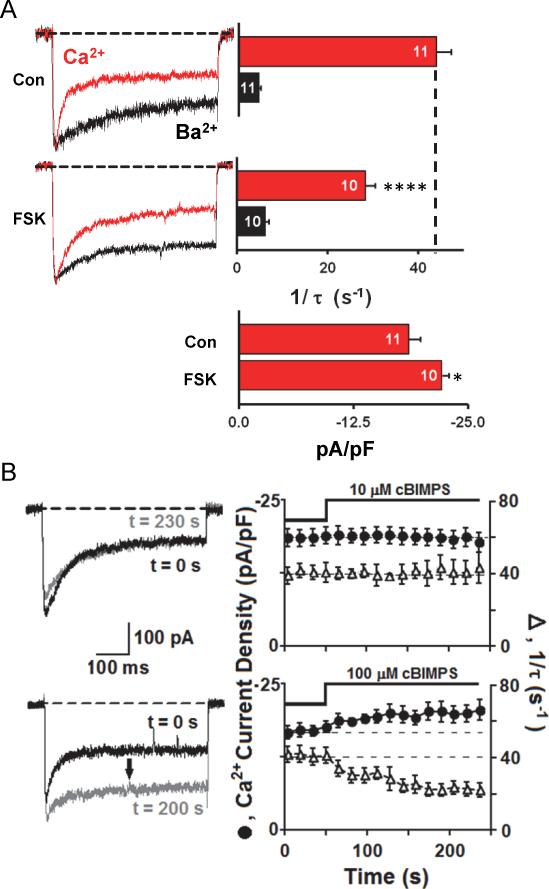
Figure. 4. CDI of neuronal L-type Ca2+ channels is reduced by PKA pathway activation.
(A) Internal perfusion with forskolin slows Ca2+-dependent inactivation of L-type current and increases current density. Peak Ca2+ current amplitude (red) was normalized to peak Ba2+ current (black) amplitude. Bar graphs present inactivation rates for Ca2+ and Ba2+ currents; number of individual cells recorded (n) is marked on each bar.
(B) Bath application of 100 μM cAMP analog (Sp-5,6-dichloro-cBIMPS) (bottom), but not 10 μM Sp-5,6-dichloro-cBIMPS (top), enhances current density and slows Ca2+-dependent inactivation. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Mean values were compared using ANOVA with a Bonferroni posthoc correction. Statistical significance marked as * p = 0.05, **** p = 0.001.