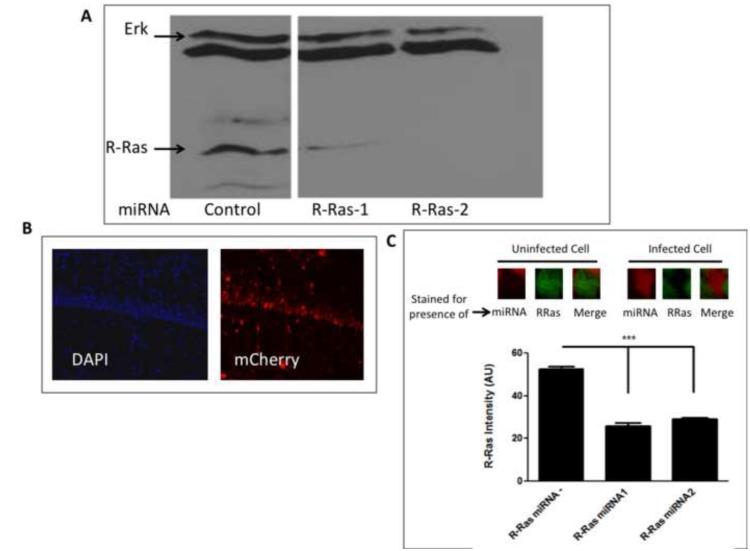
Figure 1. miRNA knockdown of R-Ras in cells and in animals.
A. Selection of R-Ras miRNAs for in vivo use. Lysates of NIH 3T3 cells transfected with two R-Ras specific miRNAs or a control unrelated miRNA sequence were immunoblotted to detect endogenous R-Ras expression. B. Expression of AAV encoding R-Ras miRNA and mCherry in the CA1 hippocampus. Hippocampal brain slices from mice infected with AAV ncoding R-Ras miRNA were stained with DAPI to detect cell nuclei and mCherry fluorescence to detect expression of virus. C. R-Ras miRNAs reduce endogenous R-Ras expression in area CA1 hippocampus. Top: Representative images of cells uninfected or infected with R-Ras miRNAs and immunostained for endogenous R-Ras. Bottom: Cells infected with either R-Ras miRNA showed significantly lower staining intensity compared to neighboring cells that were uninfected (One-way ANOVA, F 2, 512 = 112.6, p < 0.0001; Bonferroni post hoc, R-Ras miRNA - vs. R-Ras miRNA1, t = 8.40, p < 0.05, R-Ras miRNA - vs. R-Ras miRNA2, t = 13.73, p < 0.05, R-Ras miRNA1 vs. R-Ras miRNA2, t = 0.98, p > 0.05).