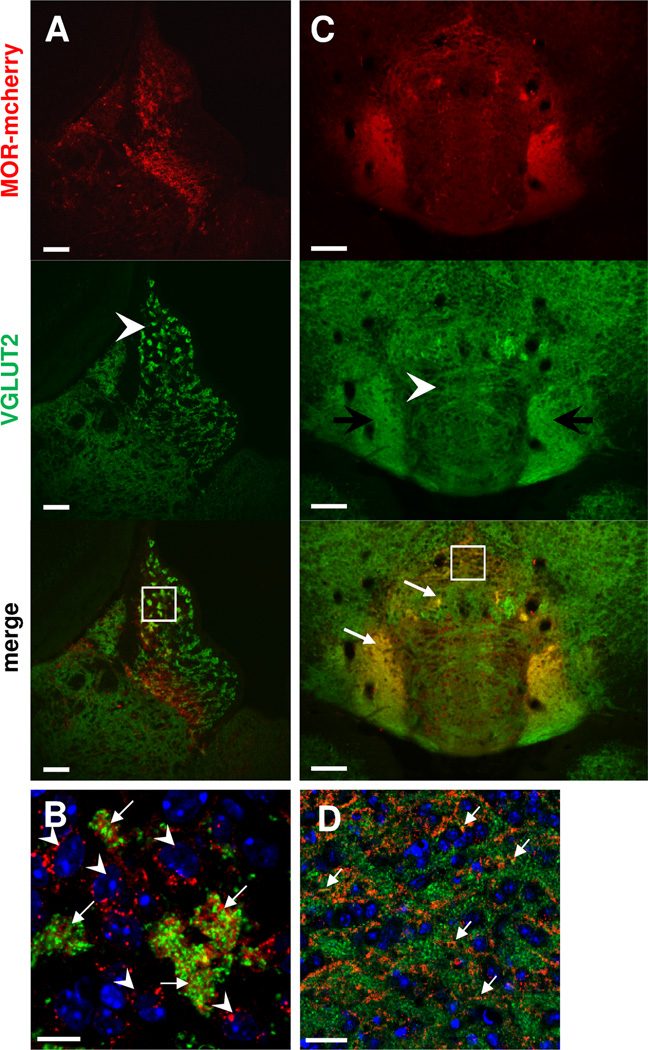
Figure 8. MOR-mcherry colocalize with VGLUT2 in the apical part of the MHb, and in the IPR and IPL.
Photomicrographs of medial habenula MHb (A–B) and interpeduncular nucleus IPN (C–D) of MOR-mcherry knock-in mice. A. Staining with antibodies directed against the vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGLUT2, green) indicates the presence of glutamatergic terminals in the MHb, with stronger staining in the apical part (arrowhead). B. Higher magnification image (white square in A) reveals co-occurrence of VGLUT2 (green) and MOR-mcherry (red) immunostaining in in-between somata spaces of the apical MHb (arrows), surrounded by MOR-mcherry expressing neurons (arrowheads). C. In the IPN, VGLUT2 is located in axons forming a cistern in the upper part of the IPI and IPC (arrowhead). Immunostaining is also found in the IPL and IPR. Colocalization with MOR-mcherry is detected in the IPL and IPR (white arrows). D. Enlargement of the IPR area delimited by a white square in C. Colocalization between VGLUT2 (green) and MOR-mcherry (red) is visible in the IPR by the presence of yellow dots (white arrows). DAPI in blue. Scale bar= 50 µm (A & C), 10 µm (B & D).