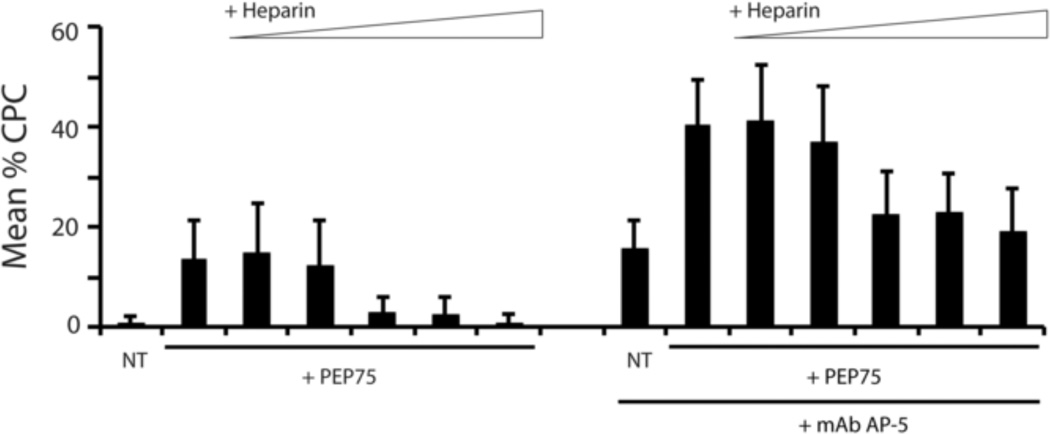
Figure 6. PEP75 induces CLAN formation which is sensitive to competition with heparin.
N27TM-2 HTM cells were plated onto fibronectin-coated coverslips in the absence or presence of 60 µg/mL (28.5 µM) PEP75 together with increasing concentrations of heparin (0.02 µM – 200µM in 10-fold increments). The treatment groups on the right half of the graph included mAb AP-5. After 3 hours the cells were fixed and labeled with phalloidin. The percentage of CPCs is shown as the mean ± the SD; n ranged from 1134–2149 cells for each treatment group. Both PEP75 and mAb AP-5 alone increased CLAN formation over untreated contols (P < 0.01). 2.0 µM, 20 µM and 200 µM concentrations of heparin decreased PEP75-induced CLAN formation to near control levels (P > 0.01) while 0.02 µM and 0.2 µM concentrations had no effect. PEP75 and AP-5 in combination induced significantly greater CLAN formation than PEP75 alone or AP-5 alone, respectively (P < 0.01). 2.0 µM, 20 µM and 200 µM heparin significantly decreased CLAN formation in cells treated with PEP75 and AP-5 to levels seen in cells treated with AP-5 alone (P < 0.01) while 0.02 µM and 0.2 µM, again, had no effect.