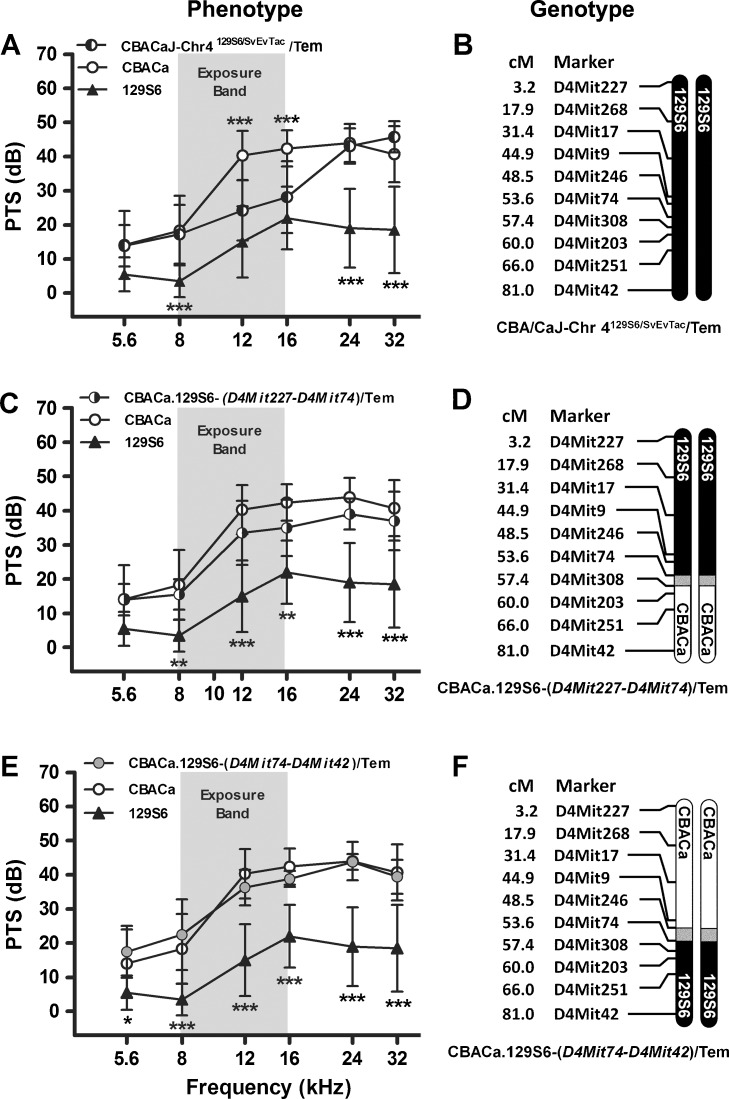
FIG. 8.
Chromosome 4 congenic strains. PTS (A, C, E) for two Chr 4 congenic strains are compared to the parental CBACa (n = 29, open circle) and 129S6 (n = 10, triangle) strains, displayed with the recombinant crossover event defining each strain (B, D, F). 129S6 and CBACa chromosomal segments are depicted by filled and open chromosomes, respectively. The gray regions represent uncharacterized DNA near the crossover point. SSLP markers used to characterize the strain and the cM (centiMorgan) position for each marker are indicated. The noise exposure band (8–16 kHz) is highlighted in gray. Data are expressed as means (±SD). A p value asterisk located above a CBACa data point represents the statistical comparison between CBACa and the consomic or congenic strain of interest, while an asterisk below a 129S6 data point represents the comparison between 129S6 and the strain. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 in a Bonferroni post hoc test following a two-way ANOVA. A 129S6 Chr 4 appears to contribute to NR at 12 and 16 kHz in the CBA/CaJ-Chr 4129S6/SvEvTac/Tem strain (n = 18). PTS data are the same as those shown in Fig. 6A, duplicated here to allow comparison between the two congenic strains generated from the CBA/CaJ-Chr 4129S6/SvEvTac/Tem consomic strain. B This consomic strain contains a nonrecombinant 129S6 Chr 4. C The NR phenotype in strain CBACa.129S6-(D4Mit227-D4Mit74)/Tem (n = 10) is not significantly different from CBACa. D This congenic strain contains a crossover between D4Mit74 and D4Mit308. E The NR phenotype in strain CBACa.129S6-(D4Mit74-D4Mit42)/Tem (n = 8) is not significantly different from CBACa. F This congenic strain is defined by a crossover between D4Mit246 and D4Mit74.