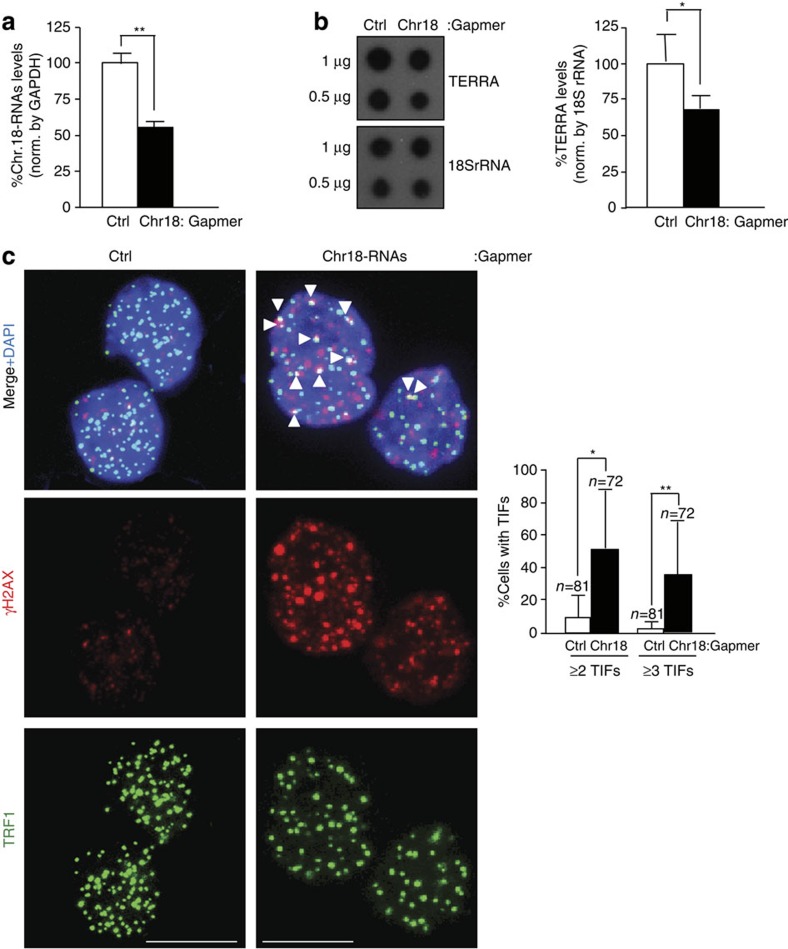
Figure 5. Downregulation of chromosome 18-TERRAs induces telomere damage.
(a) Cells were transfected with either control Gapmer-LNA (Ctrl) or Gapmer-LNA targeting chromosome 18-RNAs and RNA collected 2 days post transfection. The graph shows the percentage of chromosome 18-RNA levels normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) levels upon Gapmer-LNA transfection (mean±s.e.m.; three independent transfections). (b) (Left) RNA dot-blot to detect TERRA using a 32P-dCTP-labelled probe; hybridization of 18S rRNA was included as a loading control. (Right) Quantification of the RNA dot-blot signals normalized by 18S rRNA (mean±s.e.m.; three independent transfections). (c) Representative images of TRF1 (green) and γH2AX (red) fluorescence and of the merged images. Co-localization events (arrowheads) indicate telomere dysfunction-induced foci (TIF). Scale bar, 10 μm. (Graph) Percentage of cells with ≥2 or ≥3 TIFs/nuclei (mean±s.d., n=number of nuclei; three independent transfections). Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis (*P<0.05 and **P<0.001).