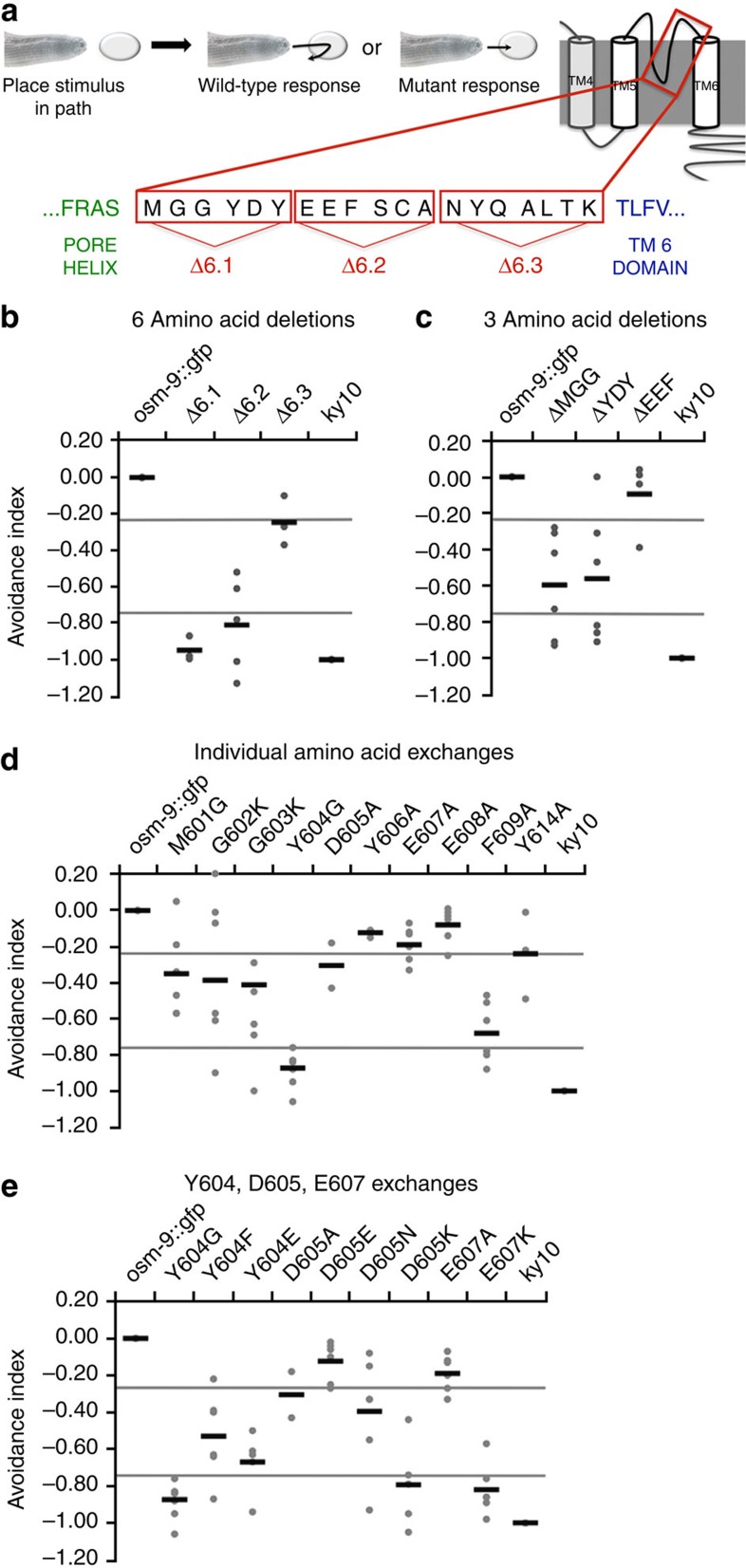
Figure 1. OSM-9 mutations result in avoidance defects mediated by ASH.
(a) Schematic of worm avoidance behaviour and loop 6 sequence of OSM-9. A quantity of 1 M fructose is dropped in the pathway of a forward-moving worm. WT worms swiftly reverse the direction after touching the aversive liquid, whereas mutant worms continue moving forward through the drop after contact. Schematic of OSM-9 protein structures and sequence C-terminal to the pore helix, before TM6, depicting orientation of 6 and 3 amino acid deletions. (b–e) Behavioral avoidance metrics for amino acid deletions and exchanges in OSM-9. Percent avoidance is acquired by averaging number of responders divided by number of animals tested from 5 to 6 worms per transgenic line, from each of three lines to give a total of 15–18 worms tested. Percent avoidance for each strain is normalized to osm-9::gfp WT rescue and osm-9 (ky10) strain values for the time point it was collected. This process is completed twice and values are averaged to produce the avoidance index. Strains with an avoidance index ≥−0.25 are considered WT, between −0.26 and −0.74 are considered partially defective, and ≤−0.75 are considered defective. Black lines represent mean of the grey dots, each grey dot represent results from 10 individual animals on a given day of testing. Each strain had three independent lines that were tested on 2 separate days.