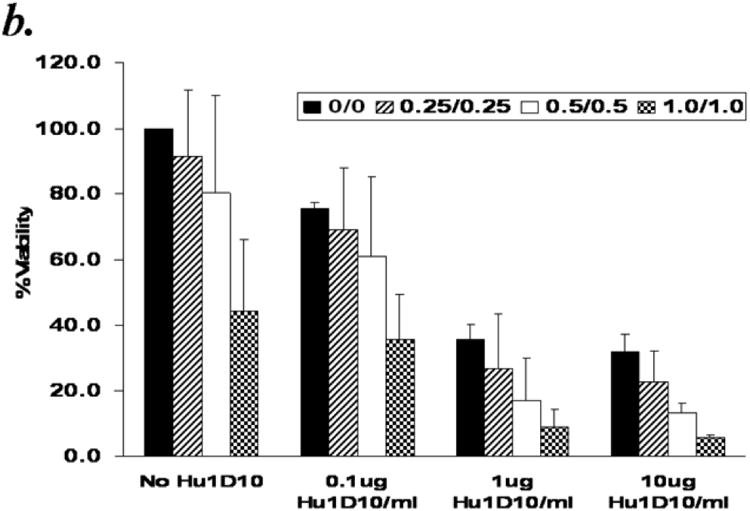
Figure 7.
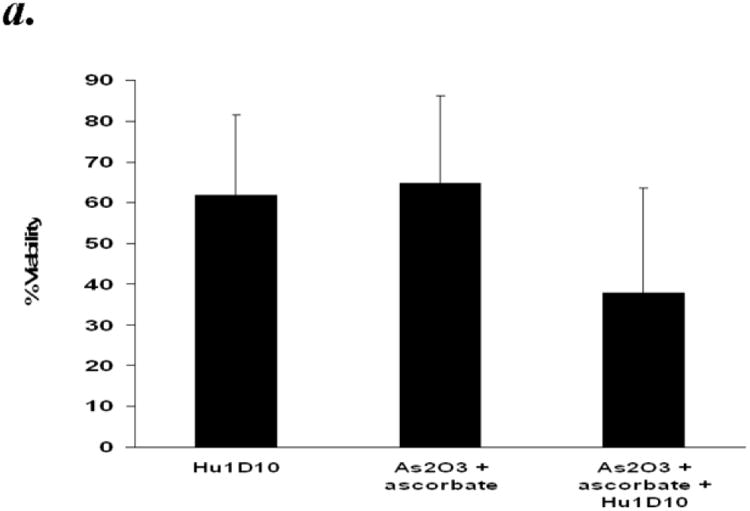
Panel a: Arsenic trioxide and ascorbic acid enhance Hu1D10 mediated cytotoxicity of primary CLL B cells. Purified B-lymphocytes from CLL patients (1×106/ml media) were treated with Hu1D10 (10ug/ml), arsenic trioxide [ATO](1μM)/ascorbic acid (1mM) or Hu1D10 and ATO/ascorbic acid. The cells were stained with Annexin-V-FITC and propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry as described above. The data shown represent % Annexin-V-/PI- viable cells ± SD that are normalized to media control. (n=11).
Panel b: Arsenic trioxide and ascorbic acid enhance the cytotoxicity of Hu1D10 in a dose dependent manner. Purified B-lymphocytes from CLL patients (1×106/ml media) were treated with indicated concentrations of Hu1D10, arsenic trioxide [ATO] and ascorbic acid. The cells were stained with Annexin-V-FITC and propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry as described above. The data shown represent % Annexin-V-/PI- viable cells ± SD that are normalized to media control. Varying arsenic trioxide/ascorbic acid and Hu1D10 concentrations show that even if Hu1D10 concentration is lowered 10 fold, the cytotoxicity in conjunction with ATO/ascorbic acid is significantly enhanced.
