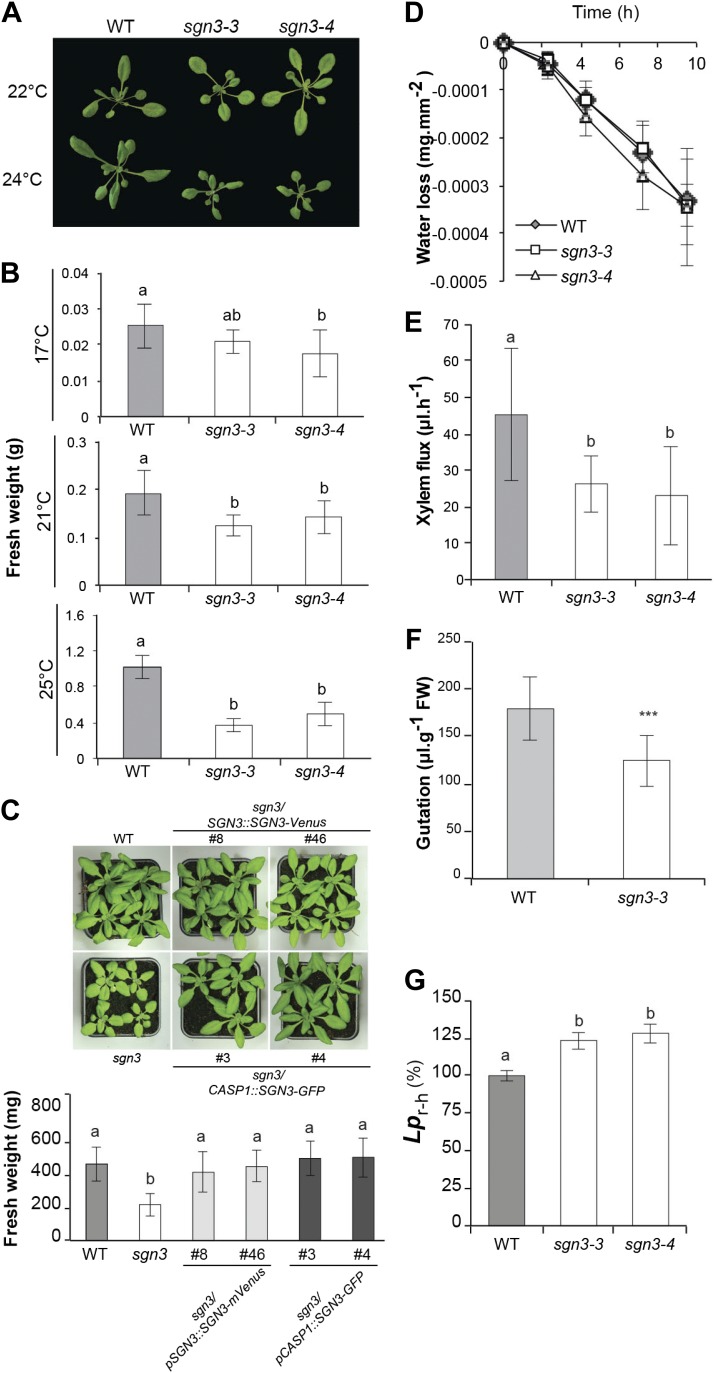
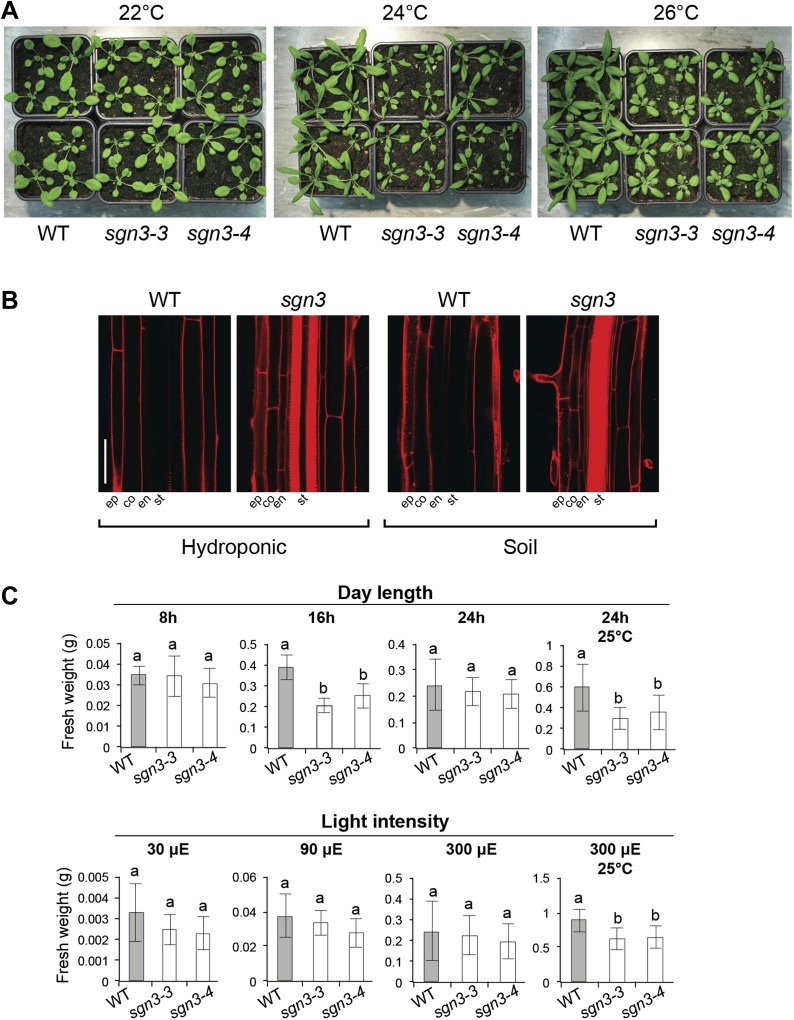
Figure 4. sgn3 is sensitive to environmental conditions and displays an altered water transport and root pressure.
(A) Phenotype of 3-week-old WT, sgn3-3, and sgn3-4 plants grown at 22 or 24°C in long days. Representative pictures are presented. (B) Analysis of shoots fresh weight of WT, sgn3-3, and sgn3-4 plants (n = 15) grown 3 weeks at different temperatures (17, 21, or 25°C). (C) Phenotype of 4-week-old WT, sgn3-3, sgn3-3/pSGN3::SGN3-mVenus (lines 8 and 46), and sgn3-3/pCASP1::SGN3-GFP (lines 3 and 4) grown at 24°C in long days. Representative pictures are presented. Fresh weight average from n > 8 plants. (D) Transpiration of WT, sgn3-3, and sgn3-4 plants determined as water loss from 3-week-old plants. Error bars = s.d. (n = 10). (E) Root pressure analysis determined as the volume of xylem sap released in 30 min from decapitated WT, sgn3-3, and sgn3-4 plants grown in short day condition (n = 7). (F) Guttation was collected from WT and sgn3-3 plants grown for 6 weeks in short day conditions (n = 15). (G) Mean hydrostatic hydraulic conductivity of roots (Lpr-h) from WT, sgn3-3, and sgn3-4 plants. Lpr-h was measured during the daytime. Values correspond to means ± SD (n > 14). B, C, E, F, G. Error bars = s.d. For multiple comparison, different letters indicate significant differences between genotypes, determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey test as post hoc analyses; (B, p < 0.01) (E, G, p < 0.05). For single comparison in F, stars (***) indicate significant difference determined by Student test (p < 0.001).