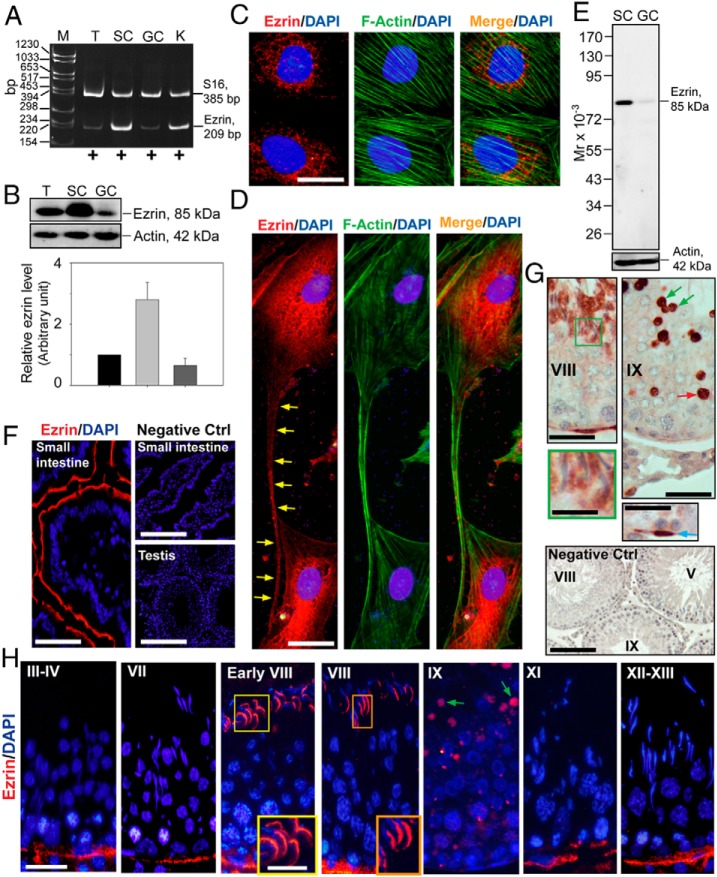
Figure 1.
A–G, Expression of ezrin by Sertoli cells and germ cells, and its stage-specific localization in the seminiferous epithelium of adult rat testes. A, Relative expression of ezrin in adult rat testis (T), Sertoli cells (SC), and germ cells (GC) vs kidney (K; served as a positive control) was analyzed by RT-PCR. S-16 served as a loading and PCR control. M, DNA size markers in base pairs. B, Lysates of testes (T) from adult rats, Sertoli cells (SC), and germ cells (GC) were used (∼30 μg protein per sample) for immunoblotting to assess the steady-state protein level of ezrin. β-Actin served as a protein loading control. Immunoblot data were summarized in this histogram, with each bar representing a mean ± SD of three samples, normalized against actin. The relative protein level of ezrin in the testis was arbitrarily set at 1. C, Dual-labeled immunofluorescence analysis to assess colocalization of ezrin (red fluorescence) with F-actin (green fluorescence) in Sertoli cells. Sertoli cell nuclei were visualized by DAPI. Scale bar, 15 μm (applies to all micrographs). D, Colocalization of ezrin (red) with F-actin (green) at the intercellular bridge (yellow arrows) between two Sertoli cells. Sertoli cell nuclei were visualized by DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 40 μm (applies to all micrographs). E, Specificity of the antiezrin antibody was assessed by immunoblotting using lysate of Sertoli (SC) and germ cells (GC). β-Actin served as a protein loading control. F, Localization of ezrin (red) in the small intestine (SI) at duodenum using frozen sections to confirm ezrin expression in the epithelial cells to serve as a positive control. Primary antibody replaced by normal mouse IgG served as a negative control. Scale bar, 120 μm on the left panel; 300 μm on the right panel. G, IHC localization of ezrin (reddish brown precipitates) in the testis, illustrating the localization of ezrin at the apical ES. Ezrin was mostly localized at the convex (dorsal) side and the tip of spermatid heads but was limited to stage VIII tubules (see enlarged boxed image). In a stage IX tubule, ezrin was detected in residual bodies (green arrows) and also phagosomes (red arrow). Leydig cells were not ezrin positive, but ezrin occasionally stained a few cells in the interstitium, apparently macrophages, as shown in this stage IX tubule; blue arrow illustrates a peritubular myoid cell stained positive for ezrin. Scale bar, 50 μm in all micrographs; scale bar 25 μm in green boxed inset. In negative control, primary antibody was replaced with normal rabbit IgG; scale bar 150 μm. H, Localization of ezrin (red) in the seminiferous epithelium of adult rat testes. Expression of ezrin at the apical ES was mostly limited to stage VIII tubules. However, at stage IX, ezrin also stained prominently with residual body. At the basal ES/BTB, ezrin was detected in all stages of the cycle except at stage IX when its expression was considerably diminished. Insets represent enlarged images of ezrin in corresponding boxed areas, illustrating ezrin was detected mostly at the convex side of spermatid heads. Scale bar, 50 μm (applies to other micrographs); scale bar, 25 μm in inset. Findings shown herein are representative data of three to five experiments.