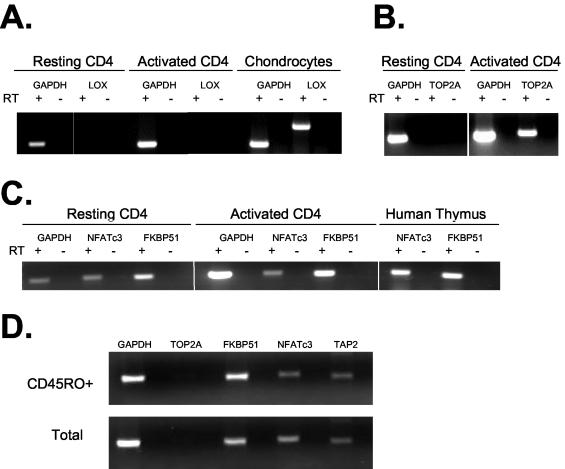
FIG. 4.
Analysis of host gene expression in resting CD4+ T cells. All transcriptional units in which an integration site was identified were analyzed by RT-PCR (Table 1). Representative examples are shown. In all three panels, GAPDH served as a positive control for RT-PCR. RT-PCRs were carried out with (+) or without (−) RT. (A) Patterns of expression of GAPDH and LOX by resting CD4+ T cells, by activated CD4+ T cells, and by chondrocytes. In all instances, RT-PCR signals were dependent on the presence of RT. (B) Expression of TOP2A by mitogen-activated but not resting CD4+ T cells. RT-PCR signals were dependent on the presence of RT. (C) Analysis of NFATc3 and FKBP51 expression in resting and activated CD4+ T cells and in the thymus. RT-PCR signals were dependent on the presence of RT. (D) Patterns of expression of genes targeted for integration in resting CD4+ T cells and in the memory subset of resting CD4+ T cells.